Study of the skin anatomy with high-frequency (22 MHz) ultrasonography and histological correlation
- PMID: 26543285
- PMCID: PMC4633078
- DOI: 10.1590/0100-3984.2014.0028
Study of the skin anatomy with high-frequency (22 MHz) ultrasonography and histological correlation
Abstract
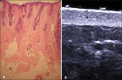
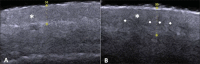
The present essay is aimed at getting the radiologist familiar with the basic histological skin structure, allowing for a better correlation with sonographic findings. A high-frequency (22 MHz) ultrasonography apparatus was utilized in the present study. The histological analysis was performed after the skin specimens fixation with formalin, inclusion in paraffin blocks and subsequent staining with hematoxylin-eosin. The authors present a literature review showing the relationship between sonographic and histological findings in normal cutaneous tissue, and discuss the technique for a better performance of the sonographic scan. High-frequency ultrasonography is an excellent tool for the diagnosis of different skin conditions. However, as this method is operator-dependent, it is crucial to understand the normal skin structure as well as the correlation between histological and sonographic findings.
O objetivo deste trabalho é familiarizar o radiologista com a estrutura histológica cutânea, o que torna possível uma melhor correlação dos achados ultrassonográficos da pele. Para o exame radiológico foi utilizado aparelho de ultrassom de alta frequência (22 MHz). O exame histológico foi realizado após fixação do material em formol, inclusão em parafina e coloração com hematoxilina-eosina. Os autores fazem uma revisão da literatura, demonstram a relação dos achados ultrassonográficos e histológicos do tecido cutâneo normal e discutem a técnica para o melhor aproveitamento do exame ultrassonográfico da pele. O ultrassom de alta frequência representa uma excelente ferramenta no diagnóstico das diferentes alterações cutâneas. Como o método é operador-dependente, é crucial o perfeito entendimento da pele normal e sua equivalência histológica/ultrassonográfica.
Keywords: Dermatology; Histology; Skin; Ultrasonography.
Figures





References
-
- Resende DAQP, Souza LRMF, Monteiro IO, et al. Scrotal collections: pictorial essay correlating sonographic with magnetic resonance imaging findings. Radiol Bras. 2014;47:43–48.
-
- Terazaki CRT, Trippia CR, Trippia CH, et al. Synovial chondromatosis of the shoulder: imaging findings. Radiol Bras. 2014;47:38–42.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
