Mechanism and pharmacological rescue of berberine-induced hERG channel deficiency
- PMID: 26543354
- PMCID: PMC4622489
- DOI: 10.2147/DDDT.S91561
Mechanism and pharmacological rescue of berberine-induced hERG channel deficiency
Erratum in
-
Erratum: Mechanism and pharmacological rescue of berberine-induced hERG channel deficiency [Corrigendum].Drug Des Devel Ther. 2016 Nov 1;10:3573. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S124104. eCollection 2016. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2016. PMID: 27843297 Free PMC article.
Abstract
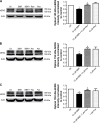
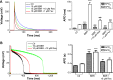
Berberine (BBR), an isoquinoline alkaloid mainly isolated from plants of Berberidaceae family, is extensively used to treat gastrointestinal infections in clinics. It has been reported that BBR can block human ether-a-go-go-related gene (hERG) potassium channel and inhibit its membrane expression. The hERG channel plays crucial role in cardiac repolarization and is the target of diverse proarrhythmic drugs. Dysfunction of hERG channel can cause long QT syndrome. However, the regulatory mechanisms of BBR effects on hERG at cell membrane level remain unknown. This study was designed to investigate in detail how BBR decreased hERG expression on cell surface and further explore its pharmacological rescue strategies. In this study, BBR decreases caveolin-1 expression in a concentration-dependent manner in human embryonic kidney 293 (HEK293) cells stably expressing hERG channel. Knocking down the basal expression of caveolin-1 alleviates BBR-induced hERG reduction. In addition, we found that aromatic tyrosine (Tyr652) and phenylalanine (Phe656) in S6 domain mediate the long-term effect of BBR on hERG by using mutation techniques. Considering both our previous and present work, we propose that BBR reduces hERG membrane stability with multiple mechanisms. Furthermore, we found that fexofenadine and resveratrol shorten action potential duration prolongated by BBR, thus having the potential effects of alleviating the cardiotoxicity of BBR.
Keywords: LQTS; berberine; cardiotoxicity; cavoline-1; hERG; pharmacological rescue.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Berberine induces hERG channel deficiency through trafficking inhibition.Cell Physiol Biochem. 2014;34(3):691-702. doi: 10.1159/000363034. Epub 2014 Aug 18. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2014. PMID: 25171176
-
Inhibitory effects and mechanism of dihydroberberine on hERG channels expressed in HEK293 cells.PLoS One. 2017 Aug 1;12(8):e0181823. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0181823. eCollection 2017. PLoS One. 2017. PMID: 28763460 Free PMC article.
-
Cyclovirobuxine D inhibits the currents of HERG potassium channels stably expressed in HEK293 cells.Eur J Pharmacol. 2011 Jun 25;660(2-3):259-67. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2011.03.039. Epub 2011 Apr 12. Eur J Pharmacol. 2011. PMID: 21497594
-
[HERG K+ channel, the target of anti-arrhythmias drugs].Yao Xue Xue Bao. 2007 Jul;42(7):687-91. Yao Xue Xue Bao. 2007. PMID: 17882949 Review. Chinese.
-
Facilitation of hERG Activation by Its Blocker: A Mechanism to Reduce Drug-Induced Proarrhythmic Risk.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Nov 13;24(22):16261. doi: 10.3390/ijms242216261. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 38003453 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Quercetin is a foe in the heart by targeting the hERG potassium channel.Iran J Basic Med Sci. 2024;27(11):1397-1404. doi: 10.22038/ijbms.2024.77846.16848. Iran J Basic Med Sci. 2024. PMID: 39386239 Free PMC article.
-
Berberine in Cardiovascular and Metabolic Diseases: From Mechanisms to Therapeutics.Theranostics. 2019 Mar 16;9(7):1923-1951. doi: 10.7150/thno.30787. eCollection 2019. Theranostics. 2019. PMID: 31037148 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Stereoselective Blockage of Quinidine and Quinine in the hERG Channel and the Effect of Their Rescue Potency on Drug-Induced hERG Trafficking Defect.Int J Mol Sci. 2016 Sep 28;17(10):1648. doi: 10.3390/ijms17101648. Int J Mol Sci. 2016. PMID: 27690007 Free PMC article.
-
hERG1 is involved in the pathophysiological process and inhibited by berberine in SKOV3 cells.Oncol Lett. 2019 Jun;17(6):5653-5661. doi: 10.3892/ol.2019.10263. Epub 2019 Apr 17. Oncol Lett. 2019. PMID: 31186788 Free PMC article.
-
Risk Compounds, Preclinical Toxicity Evaluation, and Potential Mechanisms of Chinese Materia Medica-Induced Cardiotoxicity.Front Pharmacol. 2021 Mar 30;12:578796. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.578796. eCollection 2021. Front Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 33867974 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

