Glutathione-degradable drug-loaded nanogel effectively and securely suppresses hepatoma in mouse model
- PMID: 26543363
- PMCID: PMC4622485
- DOI: 10.2147/IJN.S90000
Glutathione-degradable drug-loaded nanogel effectively and securely suppresses hepatoma in mouse model
Abstract
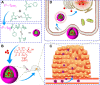
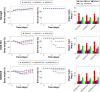
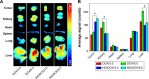
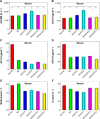
The reduction-responsive polymeric nanocarriers have attracted considerable interest because of a significantly higher concentration of intracellular glutathione in comparison with that outside cells. The smart nanovehicles can selectively transport the antitumor drugs into cells to improve efficacies and decrease side effects. In this work, a facilely prepared glutathione-degradable nanogel was employed for targeting intracellular delivery of an antitumor drug (ie, doxorubicin [DOX]). DOX was loaded into nanogel through a sequential dispersion and dialysis approach with a drug loading efficiency of 56.8 wt%, and the laden nanogel (noted as NG/DOX) showed an appropriate hydrodynamic radius of 56.1±3.5 nm. NG/DOX exhibited enhanced or improved maximum tolerated dose on healthy Kunming mice and enhanced intratumoral accumulation and dose-dependent antitumor efficacy toward H22 hepatoma-xenografted mouse model compared with free drug. In addition, the upregulated antitumor efficacy of NG/DOX was further confirmed by the histopathological and immunohistochemical analyses. Furthermore, the excellent in vivo security of NG/DOX was confirmed by the detection of body weight, histopathology, and biochemical indices of corresponding organs and serum. With controllable large-scale preparation and fascinating in vitro and in vivo properties, the reduction-responsive nanogel exhibited a good prospect for clinical chemotherapy.
Keywords: antitumor efficacy; chemotherapy; controlled release; nanogel; reduction-responsiveness; security.
Figures








Similar articles
-
Reduction-responsive polypeptide nanogel delivers antitumor drug for improved efficacy and safety.Acta Biomater. 2015 Nov;27:179-193. doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2015.08.049. Epub 2015 Aug 28. Acta Biomater. 2015. PMID: 26320542
-
Intracellularly Swollen Polypeptide Nanogel Assists Hepatoma Chemotherapy.Theranostics. 2017 Jan 15;7(3):703-716. doi: 10.7150/thno.16794. eCollection 2017. Theranostics. 2017. PMID: 28255361 Free PMC article.
-
Intratumoral Administration of Thermosensitive Hydrogel Co-Loaded with Norcantharidin Nanoparticles and Doxorubicin for the Treatment of Hepatocellular Carcinoma.Int J Nanomedicine. 2021 Jun 15;16:4073-4085. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S308057. eCollection 2021. Int J Nanomedicine. 2021. PMID: 34163160 Free PMC article.
-
Acid and reduction stimulated logic "and"-type combinational release mode achieved in DOX-loaded superparamagnetic nanogel.Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2016 Aug 1;65:354-63. doi: 10.1016/j.msec.2016.04.029. Epub 2016 Apr 16. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2016. PMID: 27157762
-
Evaluation of Polymer Nanoformulations in Hepatoma Therapy by Established Rodent Models.Theranostics. 2019 Feb 20;9(5):1426-1452. doi: 10.7150/thno.31683. eCollection 2019. Theranostics. 2019. PMID: 30867842 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Redox-sensitive micelles composed of disulfide-linked Pluronic-linoleic acid for enhanced anticancer efficiency of brusatol.Int J Nanomedicine. 2018 Feb 13;13:939-956. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S130696. eCollection 2018. Int J Nanomedicine. 2018. PMID: 29491708 Free PMC article.
-
Polypeptide Nanogels With Different Functional Cores Promote Chemotherapy of Lung Carcinoma.Front Pharmacol. 2019 Feb 4;10:37. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2019.00037. eCollection 2019. Front Pharmacol. 2019. PMID: 30778298 Free PMC article.
-
Tumor Microenvironment-Responsive Polypeptide Nanogels for Controlled Antitumor Drug Delivery.Front Pharmacol. 2021 Oct 27;12:748102. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.748102. eCollection 2021. Front Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 34776965 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Polymer Nanoformulation of Sorafenib and All-Trans Retinoic Acid for Synergistic Inhibition of Thyroid Cancer.Front Pharmacol. 2020 Feb 3;10:1676. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2019.01676. eCollection 2019. Front Pharmacol. 2020. PMID: 32116677 Free PMC article.
-
GE11 peptide modified and reduction-responsive hyaluronic acid-based nanoparticles induced higher efficacy of doxorubicin for breast carcinoma therapy.Int J Nanomedicine. 2016 Oct 7;11:5125-5147. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S113469. eCollection 2016. Int J Nanomedicine. 2016. PMID: 27785019 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Joyce JA, Fearon DT. T cell exclusion, immune privilege, and the tumor microenvironment. Science. 2015;348(6230):74–80. - PubMed
-
- Xu W, Ding J, Li L, Xiao C, Zhuang X, Chen X. Acid-labile boronate-bridged dextran-bortezomib conjugate with up-regulated hypoxic tumor suppression. Chem Commun. 2015;51(31):6812–6815. - PubMed
-
- Shi F, Ding J, Xiao C, et al. Intracellular microenvironment responsive PEGylated polypeptide nanogels with ionizable cores for efficient doxorubicin loading and triggered release. J Mater Chem. 2012;22(28):14168–14179.
-
- Ding J, Xu W, Zhang Y, et al. Self-reinforced endocytoses of smart polypeptide nanogels for “on-demand” drug delivery. J Control Release. 2013;172(2):444–455. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

