Development of hypertension in overweight adolescents: a review
- PMID: 26543386
- PMCID: PMC4622556
- DOI: 10.2147/AHMT.S55837
Development of hypertension in overweight adolescents: a review
Abstract
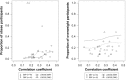
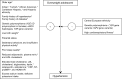
The upward trend in adolescent hypertension is widely attributed to the adolescent obesity epidemic. Secular trends in adolescent prehypertension and hypertension have risen in congruence with increasing trends in the prevalence of overweight and obesity. The correlation between body mass index and blood pressure in adolescence is moderate to strong in most studies and strongest in those classified as overweight or obese. The mechanisms relating to the development of hypertension in overweight adolescents are unclear; however, a number of nonmodifiable and modifiable factors have been implicated. Importantly, certain clinical and biochemical markers in overweight adolescents are indicative of high risk for hypertension, including family history of hypertension and hyperinsulinemia. These characteristics may prove useful in stratifying overweight adolescents as high or low risk of comorbid hypertension. The treatment of overweight and obesity related hypertension in this population focuses on two key modalities: lifestyle change and pharmacotherapy. These approaches focus almost exclusively on weight reduction; however, a number of emerging strategies target hypertension more specifically. Among adolescents with overt hypertension there are also several factors that indicate higher risk of concurrent subclinical disease, persistent adult hypertension, and adult cardiovascular disease. This group may benefit substantially from more aggressive pharmacological treatments. Limitations in the literature relate to the paucity of studies reporting specific effects for the adolescent age group of overweight and obese individuals. Nonetheless, intervention for adiposity-related hypertension in adolescence may partially mitigate some of the cardiovascular risk in adulthood.
Keywords: blood pressure; childhood; obesity; prevention; risk factors.
Figures
References
-
- La Manna A, Spagnoletti T, Galizia G, Ponticiello L, De Luca R. Statistical analysis of risk factors for hypertension in obese children. Boll Soc Ital Biol Sper. 1982;58(5):253–258. Italian. - PubMed
-
- Siklar Z, Berberoglu M, Savas Erdeve S, et al. Contribution of clinical, metabolic, and genetic factors on hypertension in obese children and adolescents. J Pediatr Endocrinol Metab. 2011;24(1–2):21–24. - PubMed
-
- Koenigsberg J, Boyd GS, Gidding SS, Hassink SG, Falkner B. Association of age and sex with cardiovascular risk factors and insulin sensitivity in overweight children and adolescents. J Cardiometab Syndr. 2006;1(4):253–258. - PubMed
-
- Harding S, Maynard MJ, Cruickshank K, Teyhan A. Overweight, obesity and high blood pressure in an ethnically diverse sample of adolescents in Britain: the Medical Research Council DASH study. Int J Obes (Lond) 2008;32(1):82–90. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

