Rational diagnoses of diabetes: the comparison of 1,5-anhydroglucitol with other glycemic markers
- PMID: 26543722
- PMCID: PMC4628038
- DOI: 10.1186/s40064-015-1389-5
Rational diagnoses of diabetes: the comparison of 1,5-anhydroglucitol with other glycemic markers
Abstract
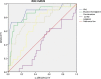
Diabetes mellitus (DM) is a frequently encountered disease with important morbidity and mortality. The aim of this study is to document the importance of 1,5-anhydroglucitol (1,5-AG) for the diagnosis of prediabetes and DM, as well as to compare the 1,5-AG with other glycemic markers in order to understand which one is the better diagnostic tool. Between April 2012 and December 2012, 128 participants enrolled in the study. Participants were split into five groups that are IFG, IGT, IFG+IGT, diabetic and control groups by their OGTT results. The diagnostic value of markers was compared by ROC (receiver operating characteristic) method. The mean serum 1,5-AG levels in the diabetic group (33.38 nmol/ml) were lower than, IFG (59.83 nmol/ml), IGT (54.44 nmol/ml), IFG+IGT (51.98 nmol/ml) and control groups (73.24 nmol/ml). When analyzed in the total study population serum 1,5-AG levels did not differ by gender significantly. When analyzed in the total study population, 1,5-AG correlates inversely with age significantly (p = 0.036). In subgroup analysis, in the control group, serum 1,5-AG level was also inversely correlated with age (p = 0.087). The best marker for the diagnosis of prediabetes and DM was fasting plasma glucose (FPG). 1,5-AG was not found to be effective for the diagnosis of DM. This study, contributes to our knowledge of the efficiency and cut-off values of 1,5-AG for the diagnosis of prediabetes and DM. In future, there is a need for larger studies with more standardized and commonly used measurement methods for 1,5-AG, in order to evaluate the efficiency of 1,5-AG for the diagnosis of prediabetes and DM.
Keywords: 1,5-Anhydroglucitol; Diabetes mellitus; Diagnosis; Fructosamine; Glycated hemoglobin; Prediabetes.
Figures
References
-
- Armbruster DA. Fructosamine: structure, analysis, and clinical usefulness. Clin Chem. 1987;33(12):2153–2163. - PubMed
-
- Frattali AL, Wolf BA. 1.5-Anhydroglucitol: a novel serum marker for screening and monitoring diabetes mellitus? Clin Chem. 1994;40(11):1991–1993. - PubMed
-
- Herman WH, Dungan KM, Wolffenbuttel BHR, Buse JB, Fahrbach JL, Jiang H, Martin S. Racial and ethnic differences in mean plasma glucose, hemoglobin A1c, and 1,5-anhydroglucitol in over 2000 patients with type 2 diabetes. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2009;94(5):1689–1694. doi: 10.1210/jc.2008-1940. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous