UFBP1, a Key Component of the Ufm1 Conjugation System, Is Essential for Ufmylation-Mediated Regulation of Erythroid Development
- PMID: 26544067
- PMCID: PMC4636156
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1005643
UFBP1, a Key Component of the Ufm1 Conjugation System, Is Essential for Ufmylation-Mediated Regulation of Erythroid Development
Abstract
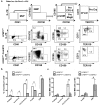
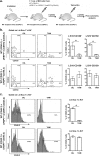
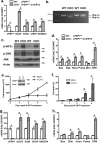
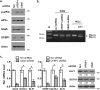
The Ufm1 conjugation system is an ubiquitin-like modification system that consists of Ufm1, Uba5 (E1), Ufc1 (E2), and less defined E3 ligase(s) and targets. The biological importance of this system is highlighted by its essential role in embryogenesis and erythroid development, but the underlying mechanism is poorly understood. UFBP1 (Ufm1 binding protein 1, also known as DDRGK1, Dashurin and C20orf116) is a putative Ufm1 target, yet its exact physiological function and impact of its ufmylation remain largely undefined. In this study, we report that UFBP1 is indispensable for embryonic development and hematopoiesis. While germ-line deletion of UFBP1 caused defective erythroid development and embryonic lethality, somatic ablation of UFBP1 impaired adult hematopoiesis, resulting in pancytopenia and animal death. At the cellular level, UFBP1 deficiency led to elevated ER (endoplasmic reticulum) stress and activation of unfolded protein response (UPR), and consequently cell death of hematopoietic stem/progenitor cells. In addition, loss of UFBP1 suppressed expression of erythroid transcription factors GATA-1 and KLF1 and blocked erythroid differentiation from CFU-Es (colony forming unit-erythroid) to proerythroblasts. Interestingly, depletion of Uba5, a Ufm1 E1 enzyme, also caused elevation of ER stress and under-expression of erythroid transcription factors in erythroleukemia K562 cells. By contrast, knockdown of ASC1, a newly identified Ufm1 target that functions as a transcriptional co-activator of hormone receptors, led to down-regulation of erythroid transcription factors, but did not elevate basal ER stress. Furthermore, we found that ASC1 was associated with the promoters of GATA-1 and Klf1 in a UFBP1-dependent manner. Taken together, our findings suggest that UFBP1, along with ASC1 and other ufmylation components, play pleiotropic roles in regulation of hematopoietic cell survival and differentiation via modulating ER homeostasis and erythroid lineage-specific gene expression. Modulating the activity of this novel ubiquitin-like system may represent a novel approach to treat blood-related diseases such as anemia.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures



References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

