Vesicle-Mediated Steroid Hormone Secretion in Drosophila melanogaster
- PMID: 26544939
- PMCID: PMC4636736
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2015.10.022
Vesicle-Mediated Steroid Hormone Secretion in Drosophila melanogaster
Abstract
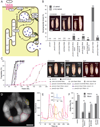
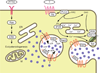
Steroid hormones are a large family of cholesterol derivatives regulating development and physiology in both the animal and plant kingdoms, but little is known concerning mechanisms of their secretion from steroidogenic tissues. Here, we present evidence that in Drosophila, endocrine release of the steroid hormone ecdysone is mediated through a regulated vesicular trafficking mechanism. Inhibition of calcium signaling in the steroidogenic prothoracic gland results in the accumulation of unreleased ecdysone, and the knockdown of calcium-mediated vesicle exocytosis components in the gland caused developmental defects due to deficiency of ecdysone. Accumulation of synaptotagmin-labeled vesicles in the gland is observed when calcium signaling is disrupted, and these vesicles contain an ABC transporter that functions as an ecdysone pump to fill vesicles. We propose that trafficking of steroid hormones out of endocrine cells is not always through a simple diffusion mechanism as presently thought, but instead can involve a regulated vesicle-mediated release process.
Copyright © 2015 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
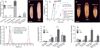



References
-
- Andrews HK, Zhang YQ, Trotta N, Broadie K. Drosophila sec10 is required for hormone secretion but not general exocytosis or neurotransmission. Traffic. 2002;3:906–921. - PubMed
-
- Aravamudan B, Fergestad T, Davis WS, Rodesch CK, Broadie K. Drosophila UNC-13 is essential for synaptic transmission. Nat Neurosci. 1999;2:965–971. - PubMed
-
- Birkenbeil H. Ultrastructural and immunocytochemical investigation of ecdysteroid secretion by the prothoracic gland of the waxmoth Galleria mellonella. Cell Tissue Res. 1983;229:433–441. - PubMed
-
- Birkenbeil H, Eckert M, Gersch M. Electron microscopical-immunocytochemical evidence of ecdysteroids in the prothoracic gland of Galleria mellonella. Cell Tissue Res. 1979;200:285–290. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

