Estrogen Receptor β Modulates Apoptosis Complexes and the Inflammasome to Drive the Pathogenesis of Endometriosis
- PMID: 26544941
- PMCID: PMC4640214
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2015.10.034
Estrogen Receptor β Modulates Apoptosis Complexes and the Inflammasome to Drive the Pathogenesis of Endometriosis
Abstract
Alterations in estrogen-mediated cellular signaling play an essential role in the pathogenesis of endometriosis. In addition to higher estrogen receptor (ER) β levels, enhanced ERβ activity was detected in endometriotic tissues, and the inhibition of enhanced ERβ activity by an ERβ-selective antagonist suppressed mouse ectopic lesion growth. Notably, gain of ERβ function stimulated the progression of endometriosis. As a mechanism to evade endogenous immune surveillance for cell survival, ERβ interacts with cellular apoptotic machinery in the cytoplasm to inhibit TNF-α-induced apoptosis. ERβ also interacts with components of the cytoplasmic inflammasome to increase interleukin-1β and thus enhance its cellular adhesion and proliferation properties. Furthermore, this gain of ERβ function enhances epithelial-mesenchymal transition signaling, thereby increasing the invasion activity of endometriotic tissues for establishment of ectopic lesions. Collectively, we reveal how endometrial tissue generated by retrograde menstruation can escape immune surveillance and develop into sustained ectopic lesions via gain of ERβ function.
Copyright © 2015 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

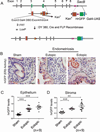

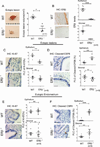
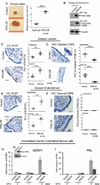
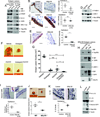
Comment in
-
Reproductive immunology: Evading immunosurveillance in endometriosis.Nat Rev Immunol. 2015 Dec;15(12):729. doi: 10.1038/nri3942. Epub 2015 Nov 16. Nat Rev Immunol. 2015. PMID: 26567919 No abstract available.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 5K12HD050128/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HD082786/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HD07857/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- P01 DK059820/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R03 HD077495/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HD007857/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HD-042311/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U19 DK062434/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U54HD0077495/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HD008188/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U54 HD007495/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HD042311/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA123125/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U54HD007495/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U19 DK62434/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- K12 HD050128/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HD08188/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

