Meta-analysis of magnetic resonance imaging for the differential diagnosis of spinal degeneration
- PMID: 26550109
- PMCID: PMC4612794
Meta-analysis of magnetic resonance imaging for the differential diagnosis of spinal degeneration
Abstract
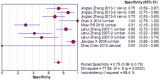
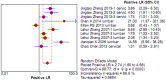
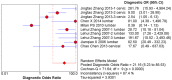
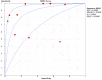
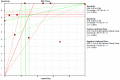
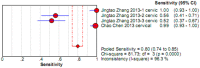
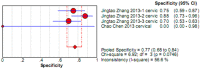
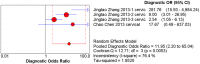
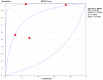
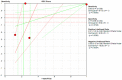
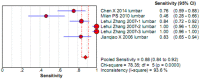
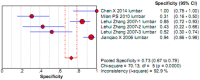
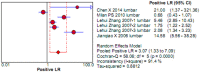
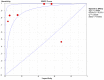
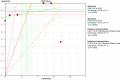
To systematically evaluate the clinical significance of magnetic resonance imaging for the identification and diagnosis of spinal degenerative changes. We searched Cochrane Library, PubMed, EMbase, CNKI, WanFang Data, Medalink, VIP and CBM databases for clinical studies on the significance of magnetic resonance imaging for the differential diagnosis of spinal degeneration; retrieval time was from database building to October 2014. Two reviewers independently screened the literature, extracted data and evaluated methodological quality according to the inclusion and exclusion criteria. Meta-DiSc 1.4 software was used for meta-analysis. The study included six documents, 10 independent results and a total of 505 individuals. Meta-analysis showed that: In the present study, the efficacy of magnetic resonance imaging in the differential diagnosis of cervical and lumbar degeneration was firstly analyzed and discussed using the Meta-Disc 1.4 software. SPE: χ(2) = 77.59, P = 0.000, I(2) = 88.4%; SEN: χ(2) = 167.25, P = 0.000, I(2) = 94.6%; DOR: Cochran-Q = 71.64, P = 0.000. Meta-analysis of random effect model showed that: SEN merge = 0.849 [95% CI (0.816,0.878)], SPE merge = 0.745 [95% CI (0.695, 0.792)], + LR = 2.735 [95% CI (1.600, -4.676)], - LR = 0.245 [95% CI (0.122, -0.493)], DOR merge = 21.158 [95% CI (5.234, -85.529)], SROC AUC = 0.8698; the results had good stability. Then the efficacy of magnetic resonance imaging in the differential diagnosis of cervical degeneration was analyzed and the results showed that: SPE: χ(2) = 6.92, P = 0.075, I(2) = 56.6%; SEN: χ(2) = 81.73, P = 0.000, I(2) = 96.3%; DOR: Cochran-Q = 12.71, P = 0.005. Meta-analysis of random effect model showed that: SEN merge = 0.799 [95% CI (0.741, 0.850)], SPE merge = 0.769 [95% CI (0.683, -0.840)], + LR = 2.506 [95% CI (1.399, -4.489)], - LR = 0.363 [95% CI (0.149, -0.882)], DOR merge = 11.949 [95% CI (2.195, -65.036)], SROC AUC = 0.8210. The stability was good. Finally, analysis of six independent studies on the efficacy of magnetic resonance imaging in the differential diagnosis of lumbar degeneration was performed: SPE: χ(2) = 70.13, P = 0.000, I(2) = 92.9%; SEN: χ(2) = 78.35, P = 0.000, I(2) = 93.6%; DOR: Cochran-Q = 58.04, P = 0.000. Meta-analysis of random effect model showed that: SEN merge = 0.732 [95% CI (0.667, -0.791)] SPE merge = 0.883 [95% CI (0.843, -0.916)], + LR = 3.072 [95% CI (1.330, -7.091)], - LR = 0.190 [95% CI (0.063, -0.572)], DOR merge = 30.252 [95% CI (3.060, -299.13)], SROC AUC = 0.8994. Sensitivity analysis was performed by excluding each study individually and the results showed no significant changes in SEN and SPE merge, indicating good stability of the meta-analysis. Existing studies confirm that MRI had good sensitivity and specificity for the differential diagnosis of cervical and lumbar degeneration; the positive ratio in cervical and lumbar degeneration group was 3 to 10 times of that in non-degeneration control group; the efficacy for differential diagnosis was good; combined with the good maneuverability in clinical diagnosis of spinal degeneration, it can be used as effective and feasible method for clinical differential diagnosis of spinal degenerative diseases.
Keywords: MRI; cervical degeneration; differential diagnosis; lumbar degeneration; meta-analysis.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Diagnostic efficacy of sentinel lymph node in breast cancer under percutaneous contrast-enhanced ultrasound: An updated meta-analysis.Thorac Cancer. 2021 Nov;12(21):2849-2856. doi: 10.1111/1759-7714.14139. Epub 2021 Oct 4. Thorac Cancer. 2021. PMID: 34605207 Free PMC article.
-
A meta-analysis on the diagnostic value of diffusion-weighted imaging on ovarian cancer.J BUON. 2019 Nov-Dec;24(6):2333-2340. J BUON. 2019. PMID: 31983103
-
Diagnostic accuracy of ultrasound superb microvascular imaging for breast tumor: a meta-analysis.Med Ultrason. 2020 Sep 5;22(3):313-318. doi: 10.11152/mu-2460. Med Ultrason. 2020. PMID: 32898204
-
Dual time point 18FDG-PET/CT versus single time point 18FDG-PET/CT for the differential diagnosis of pulmonary nodules: a meta-analysis.Acta Radiol. 2013 Sep;54(7):770-7. doi: 10.1177/0284185113481594. Epub 2013 Apr 30. Acta Radiol. 2013. PMID: 23528566
-
Use of 18F-FDG-PET/CT in differential diagnosis of primary central nervous system lymphoma and high-grade gliomas: A meta-analysis.Front Neurol. 2022 Aug 17;13:935459. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2022.935459. eCollection 2022. Front Neurol. 2022. PMID: 36061992 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Coexisting Spine Lesions on Whole Spine T2 Sagittal MRI in Evaluating Spinal Degenerative Disease.J Korean Med Sci. 2021 Feb 22;36(7):e48. doi: 10.3346/jkms.2021.36.e48. J Korean Med Sci. 2021. PMID: 33619916 Free PMC article.
-
Disc degeneration on MRI is more prevalent in young elite skiers compared to controls.Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2018 Jan;26(1):325-332. doi: 10.1007/s00167-017-4545-3. Epub 2017 Apr 13. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2018. PMID: 28409199 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Cao ZZ. Evaluate the diagnostic value of cervical degenerative disease image. Journal of Practical Medical Imaging. 2013;4:314–315.
-
- Xu C. Imaging studies of cervical facet joint sagittal angle asymmetry and its clinical significance. Southern Medical University. 2013
-
- Jia LS, Shi JG. Pay attention to cervical myelopathy diagnosis and strict surgical indications. Chinese Journal of Orthopaedics. 2002;1:57–59.
-
- Liu QY, Chen JY, Liang BL. Clinical Effect from Axially Loaded MRI Examination of Lumbar Spine. Journal of Sun Yat-sen University (Medical Sciences) 2007;3:327–331.
-
- Pan WQ. Improved diagnostic imaging study of lumbar disc degeneration sequence short time inversion recovery MRI. Third Military Medical University. 2013
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
