Accuracy and efficacy of osteotomy in total knee arthroplasty with patient-specific navigational template
- PMID: 26550129
- PMCID: PMC4612814
Accuracy and efficacy of osteotomy in total knee arthroplasty with patient-specific navigational template
Abstract
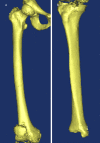
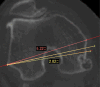
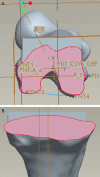
This study develops and validates a novel patient-specific navigational template for total knee arthroplasty (TKA). A total of 70 patients who underwent TKA were randomized and divided into conventional method group and navigational template group. In the navigational template group, the patient-specific navigational templates were designed and used intraoperatively to assist 35 patients with knee arthroplasty. Information on operation time and blood loss was recorded. After surgery, the positions of the prosthesis were evaluated using CT scan and X-rays. Analysis showed significant differences in errors between the two techniques. In addition, mean operation time and mean blood loss were statistically and significantly lower in the navigational template group than in the conventional group. Overall, the navigational template method showed a high degree of accuracy and efficacy.
Keywords: Total knee arthroplasty; custom template; navigation; rapid prototyping.
Figures

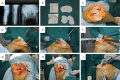
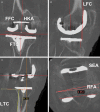
Similar articles
-
Application of Personalized Navigation Templates to Oxford Single Condylar Replacement in a Chinese Population.J Knee Surg. 2021 Sep;34(11):1155-1161. doi: 10.1055/s-0040-1702188. Epub 2020 Mar 6. J Knee Surg. 2021. PMID: 32143216 Clinical Trial.
-
Novel patient-specific navigational template for total knee arthroplasty.Comput Aided Surg. 2011;16(6):288-97. doi: 10.3109/10929088.2011.621214. Comput Aided Surg. 2011. PMID: 21992188
-
Alignment of the lower extremity mechanical axis by computer-aided design and application in total knee arthroplasty.Int J Comput Assist Radiol Surg. 2016 Oct;11(10):1881-90. doi: 10.1007/s11548-016-1382-7. Epub 2016 Mar 26. Int J Comput Assist Radiol Surg. 2016. PMID: 27017501 Clinical Trial.
-
Comparison of iASSIST Navigation System with Conventional Techniques in Total Knee Arthroplasty: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Radiographic and Clinical Outcomes.Orthop Surg. 2019 Dec;11(6):985-993. doi: 10.1111/os.12550. Epub 2019 Nov 22. Orthop Surg. 2019. PMID: 31755245 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy and reliability of active robotic-assisted total knee arthroplasty compared with conventional total knee arthroplasty: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Postgrad Med J. 2019 Mar;95(1121):125-133. doi: 10.1136/postgradmedj-2018-136190. Epub 2019 Feb 26. Postgrad Med J. 2019. PMID: 30808721 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Fidelity of 3D Printed Brains from MRI Scan in Children with Pathology (Prior Hypoxic Ischemic Injury).J Digit Imaging. 2023 Feb;36(1):17-28. doi: 10.1007/s10278-022-00723-7. Epub 2022 Oct 24. J Digit Imaging. 2023. PMID: 36280655 Free PMC article.
-
3D-printing techniques in a medical setting: a systematic literature review.Biomed Eng Online. 2016 Oct 21;15(1):115. doi: 10.1186/s12938-016-0236-4. Biomed Eng Online. 2016. PMID: 27769304 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical efficacy and effectiveness of 3D printing: a systematic review.BMJ Open. 2017 Dec 21;7(12):e016891. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2017-016891. BMJ Open. 2017. PMID: 29273650 Free PMC article.
-
Additive Manufacturing of 3D Anatomical Models-Review of Processes, Materials and Applications.Materials (Basel). 2023 Jan 16;16(2):880. doi: 10.3390/ma16020880. Materials (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36676617 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Patient-specific instrumentation improved axial alignment of the femoral component, operative time and perioperative blood loss after total knee arthroplasty.Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2019 Apr;27(4):1083-1095. doi: 10.1007/s00167-018-5256-0. Epub 2018 Oct 30. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2019. PMID: 30377714 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Gan Y, Xu D, Lu S, Ding J. Novel patient-specific navigational template for total knee arthroplasty. Comput Aided Surg. 2011;16:288–297. - PubMed
-
- Gan Y, Xu D, Lu S. Simulation study of the digitized navigation template-assisted total knee replacement. Chin J Orthop. 2011;31:964.
-
- Stulberg SD. How accurate is current TKR instrumentation? Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2003:177–184. - PubMed
-
- Jenny JY, Boeri C. Low reproducibility of the intra-operative measurement of the transepicondylar axis during total knee replacement. Acta Orthop Scand. 2004;75:74–77. - PubMed
-
- Delp SL, Stulberg SD, Davies B, Picard F, Leitner F. Computer assisted knee replacement. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1998:49–56. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
