Glucocorticoids offer protection against myocardial injury in a murine model of sepsis
- PMID: 26550131
- PMCID: PMC4612816
Glucocorticoids offer protection against myocardial injury in a murine model of sepsis
Abstract
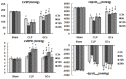
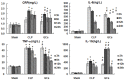
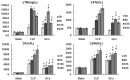
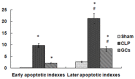
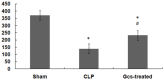
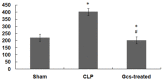
Sepsis is a serious infection-related complication that, in causing significant inflammation, often leads to myocardial injury. Severe inflammation, including in sepsis, is sometimes treated with exogenous glucocorticoids (GCs). Here, to explore the potential effect of GCs to protect against myocardial injury, we created a model of sepsis in rats by performing cecal ligation and puncture (CLP) in 96 rats randomly divided into sham-operated control (N=32), untreated sepsis (CLP, N=32), and GC-treated sepsis (N=32) groups. At 3, 6, 12, and 24 h after surgery, the changes in cardiac hemodynamic indexes, serum inflammatory response factor levels, and myocardial enzymes were measured, along with mitochondrial membrane potential in myocardial cells, apoptosis of myocardial cells, and the expression of nuclear factor kappa B (NF-κB p65) in myocardial tissues. Pathological changes in myocardial cells were also observed. Compared to the sham-operated group, CLP rats experienced deterioration of left ventricular systolic pressure (LVSP), left ventricular end-diastolic pressure (LVEDP), maximum rate of left ventricular pressure rise (+dP/dtmax), and the maximum rate of left ventricular pressure drop (-dP/dtmax). CLP rats also had a rise in serum tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α), interleukin-6 (IL-6), C-reactive protein (CRP), cardiac troponin I (cTnI), creatine kinase (CK), lactate dehydrogenase (LDH), aspartate aminotransferase (AST), and NF-κB p65 in myocardial tissues. The GCs-treated group had lower levels of these inflammatory response molecules than the CLP group, with the exception of anti-inflammatory cytokine interleukin-10 (IL-10), which was higher in the GC-treated rats than the CLP group at each time point post-surgery. Compared to the sham group, CLP rats had a rise in myocardial cell apoptosis and a drop in mitochondrial membrane potential in myocardial cells. In addition, GCs-treated rats had a marked drop in the myocardial cell apoptosis rate and a rise in the mitochondrial membrane potential compared to CLP rats. After intervention with GCs, the pathological changes in heart tissues were also reduced compared to those in the sepsis group. Based on these results, we conclude that exogenous GCs can inhibit a drop in myocardial mitochondrial membrane potential and inhibit myocardial cell apoptosis by blocking the activation of NF-κB, decreasing the generation of proinflammatory cytokines, and relieving inflammatory injury in heart tissues.
Keywords: Myocardial injury; apoptosis; mitochondrial membrane potential; nuclear transcription factor; rat.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Astragaloside IV Attenuates Polymicrobial Sepsis-Induced Cardiac Dysfunction in Rats via IKK/NF-κB Pathway.Chin J Integr Med. 2021 Nov;27(11):825-831. doi: 10.1007/s11655-021-2869-9. Epub 2021 Aug 25. Chin J Integr Med. 2021. PMID: 34432200
-
[Effect of neuregulin-1 on heart function and inflammatory mediators in rats with sepsis].Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2018 Feb;30(2):140-144. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.2095-4352.2018.02.009. Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2018. PMID: 29402363 Chinese.
-
[β1 receptor blocker decreases the myocardial inflammation in the sepsis adult rats through inhibition of TLR4/NF-ΚB signaling pathway].Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2019 Feb;31(2):193-197. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.2095-4352.2019.02.014. Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2019. PMID: 30827308 Chinese.
-
Role of activating the nuclear factor kappa B signaling pathway in the development of septic cardiomyopathy in rats with sepsis.Technol Health Care. 2023;31(5):1671-1681. doi: 10.3233/THC-220471. Technol Health Care. 2023. PMID: 37092189
-
Systematic review and meta-analysis of the interventional effects of resveratrol in a rat model of myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury.Front Pharmacol. 2024 Jan 19;15:1301502. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1301502. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38313308 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Exploring the beneficial role of telmisartan in sepsis-induced myocardial injury through inhibition of high-mobility group box 1 and glycogen synthase kinase-3β/nuclear factor-κB pathway.Korean J Physiol Pharmacol. 2020 Jul 1;24(4):311-317. doi: 10.4196/kjpp.2020.24.4.311. Korean J Physiol Pharmacol. 2020. PMID: 32587125 Free PMC article.
-
Glucocorticoid Treatment in Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome: An Overview on Mechanistic Insights and Clinical Benefit.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jul 28;24(15):12138. doi: 10.3390/ijms241512138. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37569514 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MicroRNA-181b Inhibits Inflammatory Response and Reduces Myocardial Injury in Sepsis by Downregulating HMGB1.Inflammation. 2021 Aug;44(4):1263-1273. doi: 10.1007/s10753-020-01411-w. Epub 2021 Jun 2. Inflammation. 2021. PMID: 34076811
-
Resolvin D1 Promotes SIRT1 Expression to Counteract the Activation of STAT3 and NF-κB in Mice with Septic-Associated Lung Injury.Inflammation. 2018 Oct;41(5):1762-1771. doi: 10.1007/s10753-018-0819-2. Inflammation. 2018. PMID: 30014231
References
-
- Arai K, Lee K, Berthiaume F, Tompkins RG, Yarmush ML. Intrahepatic amino acid and glucose metabolism in a D-galactosamine-induced rat liver failure model. Hepatology. 2001;34:360–371. - PubMed
-
- Bitton A, Buie D, Enns R, Feagan BG, Jones JL, Marshall JK, Whittaker S, Griffiths AM, Panaccione R. Canadian Association of Gastro- enterology Severe Ulcerative Colitis Consensus Group. Treatment of Hospitalized Adult Patients With Severe Ulcerative Colitis: Toronto Consensus Statements. Am J Gastroenterol. 2012;107:179–194. - PubMed
-
- Sakai H, Park SS, Kikkawa Y. Differential oxidase activity of hepatic and pulmonary microsomal cytochrome P-450 isozymes after treatment with cytochrome P-450 inducers. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1992;187:1262–1269. - PubMed
-
- Cheifetz AS, Stern J, Garud S, Goldstein E, Malter L, Moss AC, Present DH. Cyclosporine is safe and effective in patients with severe ulcerative colitis. J Clin Gastroenterol. 2011;45:107–112. - PubMed
-
- Rahman TM, Selden AC, Hodgson HJ. A novel model of acetaminophen-induced acute hepatic failure in rabbits. J Surg Res. 2002;106:264–272. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
