Expansion of CD14(+)CD16(+) monocytes is related to acute leukemia
- PMID: 26550139
- PMCID: PMC4612824
Expansion of CD14(+)CD16(+) monocytes is related to acute leukemia
Abstract
Objective: Aim to investigate the proportion of CD14(+)CD16(+) monocytes and understand the pathogenesis of this monocyte subset in acute leukemia.
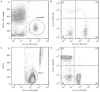
Methods: Flow cytometry was utilized to study the phenotype expression of CD14(+)CD16(+) monocytes and CD3(+) T lymphocytes in peripheral blood derived from patients with acute leukemia. All the data were analyzed by SPSS 13.0 software.
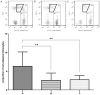
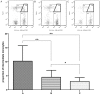
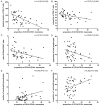
Results: The proportion of CD14(+)CD16(+) monocytes including both intermediate and non-classical monocytes, increased significantly in patients with acute leukemia and changed negatively or positively according to the disease process. Meanwhile, the proportion of CD14(+)CD16(+) monocytes was inversely correlated with absolute number of CD4(+) T lymphocytes, ratio of CD4(+)/CD8(+) T cells, and positively correlated with the proportion of neutrophil granulocytes.
Conclusions: The proportion of CD14(+)CD16(+) monocytes (especially the intermediate subpopulation) is related to the progression of acute leukemia, and the expansion of this monocyte subset could indicate the severity of the disease.
Keywords: Acute leukemia; T lymphocyte; inflammation; monocyte subset.
Figures


References
-
- Volk HD, Reinke P, Docke WD. Clinical aspects: from systemic inflammation to ‘immunoparalysis’. Chem Immunol. 2000;74:162–177. - PubMed
-
- Dayyani F, Belge KU, Frankenberger M, Mack M, Berki T, Ziegler-Heitbrock L. Mechanism of glucocorticoid-induced depletion of human CD14+CD16+ monocytes. J Leukoc Biol. 2003;74:33–39. - PubMed
-
- Passlick B, Flieger D, Ziegler-Heitbrock HW. Identification and characterization of a novel monocyte subpopulation in human peripheral blood. Blood. 1989;74:2527–2534. - PubMed
-
- Mobley JL, Leininger M, Madore S, Baginski TJ, Renkiewicz R. Genetic evidence of a functional monocyte dichotomy. Inflammation. 2007;30:189–197. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
