Bone mesenchymal stem cells overexpressing FGF4 contribute to liver regeneration in an animal model of liver cirrhosis
- PMID: 26550191
- PMCID: PMC4612876
Bone mesenchymal stem cells overexpressing FGF4 contribute to liver regeneration in an animal model of liver cirrhosis
Abstract
It is recognized that Fibroblast Growth Factor 4 (FGF-4) could not only increase the proliferation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells (BMSCs), but also induce BMSCs into hepatocyte-like cells in vitro. However, the role of FGF4 played in liver regeneration in vivo is unclear. This study constructed FGF4 overexpressing BMSCs and then transplanted them into cirrhotic rats to investigate the role of FGF4 played in liver regeneration. The results showed that FGF4 promoted the location of the BMSCs only at the early stage, and more proliferating cell nuclear antigen (PCNA), epithelial cell adhesion molecule (EpCAM) and Jagged-1 positive hepatocytes were found in the cirrhotic rats. This study indicated that FGF4 transduced BMSCs contributed to liver regeneration might by the transplanted microenvironment.
Keywords: BMSCs; microenvironment Introduction; migration; proliferation; transplant.
Figures
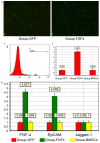
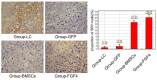
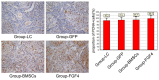
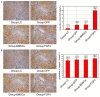
References
-
- Liu J, Fan D. Hepatitis B in China. Lancet. 2007;369:1582–1583. - PubMed
-
- Fouraschen SM, Pan Q, de Ruiter PE, Farid WR, Kazemier G, Kwekkeboom J, Ijzermans JN, Metselaar HJ, Tilanus HW, de Jonge J, van der Laan LJ. Secreted factors of human liver-derived mesenchymal stem cells promote liver regeneration early after partial hepatectomy. Stem Cells Dev. 2012;21:2410–2419. - PubMed
-
- Stock P, Brückner S, Ebensing S, Hempel M, Dollinger MM, Christ B. The generation of hepatocytes from mesenchymal stem cells and engraftment into murine liver. Nat Protoc. 2010;5:617–627. - PubMed
-
- Li J, Zhang L, Xin J, Jiang L, Li J, Zhang T, Jin L, Li J, Zhou P, Hao S, Cao H, Li L. Immediate intraportal transplantation of human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells prevents death from fulminant hepatic failure in pigs. Hepatology. 2012;56:1044–1052. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
