Effect of GABA on blood pressure and blood dynamics of anesthetic rats
- PMID: 26550413
- PMCID: PMC4613098
Effect of GABA on blood pressure and blood dynamics of anesthetic rats
Abstract
Background: This study aimed to investigate GABA effects on blood pressure and blood dynamics of anesthetic rats by observing spontaneously hypertensive rats under both anesthesia and waking state.
Materials and methods: 72 male waking Wistar-Kyokos (WKY) rats and 72 male anesthetized spontaneously hypertensive (SHR) rats were randomly divided into control group and experimental group (N = 36 each). Rats were further divided into three subgroups (N = 12 each), which received 15 μmol GABA, 35 nmol muscimol, or 4 nmol dicentrine into unilateral paraventricular nucleus, respectively. Rats in the control group (WKY1) and experimental group (SHR1) were compared for the GABA effect on blood pressure (MAP), heart rate (HR), and arterial baroreceptor reflex function (BRS) changes under waking state. Anesthetic WKY rats (WKY2) and spontaneously hypertensive rats (SHR2) were compared for the GABA effect on those abovementioned indexes. Abdominal aorta mean arterial pressure, heart rate, and arterial baroreceptor reflex function changes were compared in all rats.
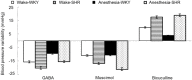
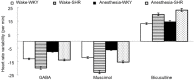
Results: MAP, HR, and BRS were slightly lower in the rats under anesthetic state than in waking state before treatment (P < 0.05); they did not show significant changes between anesthetic and waking state, however, after treatment (P > 0.05). Unilateral paraventricular nucleus injection of GABA or muscimol elevated MAP, HR, and BRS in both normal and spontaneously hypertensive rats under waking or anesthetic state (P < 0.05). In addition, the amplitudes of changes of three indicators in spontaneously hypertensive group were markedly higher than those of control group (P < 0.05). Dicentrine could induce MAP and HR to increase, while BRS decreased significantly (P < 0.05). The amplitudes of changes in spontaneously hypertensive group were larger than those of normal group (P < 0.05).
Conclusion: Centrally GABA injection can enhance the BRS function in spontaneously hypertensive rats and adjust heart rate to reduce the blood pressure fluctuation. It may play a role in reducing blood pressure and protecting cardiovascular function.
Keywords: arterial baroreceptor reflex function; blood dynamics; blood pressure; cardiovascular; γ-aminobutiric acid.
Figures

References
-
- Yalcin M, Cavun S, Yilmaz MS, Savci V. The involvement of central cholinergic system in the pressor effect of intracerebroventricularly injected U-46619, a thromboxane A2 analog, in conscious normotensive rats. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2005;372:31–40. - PubMed
-
- Root AR, Sanford JD, Kavanaugh SI, Sower SA. In vitro and in vivo effects of GABA, muscimol, and bicuculline on lamprey GnRH concentration in the brain of the sea lamprey (Petromyzon marinus) Comp Biochem Physiol A Mol Integr Physiol. 2004;138:493–501. - PubMed
-
- Wang J, Shen FM, Wang MW, Su DF. Effects of nine antihypertensive drugs on blood pressure variability in sinoaortic-denervated rats. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2006;27:1013–1017. - PubMed
-
- Gu XW, Xie HH, Wang J, Shen FM, Su DF. Arterial baroreflex is not involved in salt preference in rats. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 2006;33:607–611. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
