Glutamine may repress the weak LPS and enhance the strong heat shock induction of monocyte and lymphocyte HSP72 proteins but may not modulate the HSP72 mRNA in patients with sepsis or trauma
- PMID: 26550577
- PMCID: PMC4621332
- DOI: 10.1155/2015/806042
Glutamine may repress the weak LPS and enhance the strong heat shock induction of monocyte and lymphocyte HSP72 proteins but may not modulate the HSP72 mRNA in patients with sepsis or trauma
Abstract
Objective: We assessed the lipopolysaccharide (LPS) or heat shock (HS) induction of heat shock protein-72 (HSP72) in peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) of patients with severe sepsis (SS) or trauma-related systemic inflammatory response syndrome (SIRS), compared to healthy individuals (H); we also investigated any pre- or posttreatment modulating glutamine (Gln) effect.
Methods: SS (11), SIRS (10), and H (19) PBMCs were incubated with 1 μg/mL LPS or 43°HS. Gln 10 mM was either added 1 h before or 1 h after induction or was not added at all. We measured monocyte (m), lymphocyte (l), mRNA HSP72, HSP72 polymorphisms, interleukins (ILs), monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 (MCP-1), and cortisol levels.
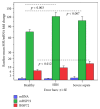
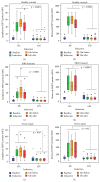
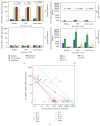
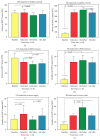
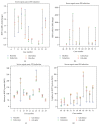
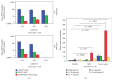
Results: Baseline lHSP72 was higher in SS (p < 0.03), and mHSP72 in SIRS (p < 0.02), compared to H. Only HS induced l/mHSP72/mRNA HSP72; LPS induced IL-6, IL-8, IL-10, and MCP-1. Induced mRNA was related to l/mHSP72, and was related negatively to cytokines. Intracellular l/mHSP72/HSP72 mRNA was related to serum ILs, not being influenced by cortisol, illness severity, and HSP72 polymorphisms. Gln did not induce mRNA in any group but modified l/mHSP72 after LPS/HS induction unpredictably.
Conclusions: HSP72 mRNA and l/mHSP72 are higher among critically ill patients, further induced by HS, not by LPS. HSP72 proteins and HSP72 mRNA are related to serum ILs and are negatively related to supernatant cytokines, not being influenced by HSP72 polymorphisms, cortisol, or illness severity. Gln may depress l/mHSP72 after LPS exposure and enhance them after HS induction, but it may not affect early induced HSP72 mRNA.
Figures

References
-
- O'Grady N. P., Barie P. S., Bartlett J. G., et al. Guidelines for evaluation of new fever in critically ill adult patients: 2008 update from the American College of Critical Care Medicine and the Infectious Diseases Society of America. Critical Care Medicine. 2008;36(4):1330–1349. doi: 10.1097/ccm.0b013e318169eda9. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

