Genetic fine mapping and genomic annotation defines causal mechanisms at type 2 diabetes susceptibility loci
- PMID: 26551672
- PMCID: PMC4666734
- DOI: 10.1038/ng.3437
Genetic fine mapping and genomic annotation defines causal mechanisms at type 2 diabetes susceptibility loci
Abstract
We performed fine mapping of 39 established type 2 diabetes (T2D) loci in 27,206 cases and 57,574 controls of European ancestry. We identified 49 distinct association signals at these loci, including five mapping in or near KCNQ1. 'Credible sets' of the variants most likely to drive each distinct signal mapped predominantly to noncoding sequence, implying that association with T2D is mediated through gene regulation. Credible set variants were enriched for overlap with FOXA2 chromatin immunoprecipitation binding sites in human islet and liver cells, including at MTNR1B, where fine mapping implicated rs10830963 as driving T2D association. We confirmed that the T2D risk allele for this SNP increases FOXA2-bound enhancer activity in islet- and liver-derived cells. We observed allele-specific differences in NEUROD1 binding in islet-derived cells, consistent with evidence that the T2D risk allele increases islet MTNR1B expression. Our study demonstrates how integration of genetic and genomic information can define molecular mechanisms through which variants underlying association signals exert their effects on disease.
Conflict of interest statement
V.Steinthorsdottir, G.T., A.K., U.T., and K.Stefansson are employed by deCODE Genetics/Amgen inc. I.B. and spouse own stock in GlaxoSmithKline and Incyte.
Figures
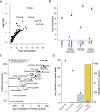
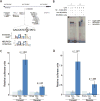
Comment in
-
Diabetes in the post-GWAS era.Nat Genet. 2015 Dec;47(12):1373-4. doi: 10.1038/ng.3453. Nat Genet. 2015. PMID: 26620109
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 HL059367/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 HG000040/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- K24 DK080140/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- G0601261/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- R01HL086694/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK093757/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK078616/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100012C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- AG04563/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- UL1RR025005/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK073490/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100009I/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- 098017/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- R01 DK058845/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- RG/08/008/25291/BHF_/British Heart Foundation/United Kingdom
- Z01 HG000024/ImNIH/Intramural NIH HHS/United States
- K24DK080140/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01HL59367/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100010C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- AG10175/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK085545/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100008C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HG065403/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR025005/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- N02 HL064278/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- 086596/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- R01DK078616/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100005G/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100008I/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100007C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P01 CA055075/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK098032/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- PG/11/4/28645/BHF_/British Heart Foundation/United Kingdom
- U01DK085526/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- AG028555/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK072193/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC025195/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100011I/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100011C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL086694/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- DK58845/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG008724/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U01HG004399/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268200625226C/PHS HHS/United States
- U01 HG004402/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- 1Z01HG000024/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- 083948/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- R01DK062370/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- 083270/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- MC_UU_12015/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- R01 DK062370/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- 072960/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- R01 DK101478/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- 101033/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- U01HG004402/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- MC_U106179471/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- MR/L02036X/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- 076113/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- R01 AG028555/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- 090367/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- HHSN268201100006C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- MC_UU_12015/2/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- 098051/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- N01 HC025195/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- MC_U106179472/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- R01HL087641/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01DK073490/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100005I/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- 090532/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- U01 DK085526/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- G0000649/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- AG08861/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- DK085545/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK078616/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- 098395/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- AG08724/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- DK098032/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK062370/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01DK072193/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100009C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100005C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK020572/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100007I/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- RG/14/5/30893/BHF_/British Heart Foundation/United Kingdom
- G116/165/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- CA055075/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- GR072960/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- 095101/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- 098381/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- R01 HL087641/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG010175/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HG004399/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

