Rabbit antithymocyte globulin-induced serum sickness disease and human kidney graft survival
- PMID: 26551683
- PMCID: PMC4665787
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI82267
Rabbit antithymocyte globulin-induced serum sickness disease and human kidney graft survival
Abstract
Background: Rabbit-generated antithymocyte globulins (ATGs), which target human T cells, are widely used as immunosuppressive agents during treatment of kidney allograft recipients. However, ATGs can induce immune complex diseases, including serum sickness disease (SSD). Rabbit and human IgGs have various antigenic differences, including expression of the sialic acid Neu5Gc and α-1-3-Gal (Gal), which are not synthesized by human beings. Moreover, anti-Neu5Gc antibodies have been shown to preexist and be elicited by immunization in human subjects. This study aimed to assess the effect of SSD on long-term kidney allograft outcome and to compare the immunization status of grafted patients presenting with SSD following ATG induction treatment.
Methods: We analyzed data from a cohort of 889 first kidney graft recipients with ATG induction (86 with SSD [SSD(+)] and 803 without SSD [SSD(-)]) from the Données Informatisées et Validées en Transplantation data bank. Two subgroups of SSD(+) and SSD(-) patients that had received ATG induction treatment were then assessed for total anti-ATG, anti-Neu5Gc, and anti-Gal antibodies using ELISA assays on sera before and after transplantation.
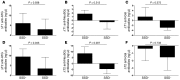
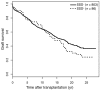
Results: SSD was significantly associated with long-term graft loss (>10 years, P = 0.02). Moreover, SSD(+) patients exhibited significantly elevated titers of anti-ATG (P = 0.043) and anti-Neu5Gc (P = 0.007) IgGs in late post-graft samples compared with SSD(-) recipients.
Conclusion: In conclusion, our data indicate that SSD is a major contributing factor of late graft loss following ATG induction and that anti-Neu5Gc antibodies increase over time in SSD(+) patients.
Funding: This study was funded by Société d'Accélération du Transfert de Technologies Ouest Valorisation, the European FP7 "Translink" research program, the French National Agency of Research, Labex Transplantex, the Natural Science and Engineering Research Council of Canada, and the Canadian Foundation for Innovation.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Rabbit antithymocyte globulin compared with basiliximab in kidney transplantation: a single-center study.Transplant Proc. 2012 Jan;44(1):167-70. doi: 10.1016/j.transproceed.2011.12.063. Transplant Proc. 2012. PMID: 22310606
-
Quantitative and qualitative changes in anti-Neu5Gc antibody response following rabbit anti-thymocyte IgG induction in kidney allograft recipients.Eur J Clin Invest. 2019 Apr;49(4):e13069. doi: 10.1111/eci.13069. Epub 2019 Feb 25. Eur J Clin Invest. 2019. PMID: 30620396
-
Evaluating safety and efficacy of rabbit antithymocyte globulin induction in elderly kidney transplant recipients.Exp Clin Transplant. 2013 Jun;11(3):222-8. doi: 10.6002/ect.2012.0211. Epub 2013 Feb 22. Exp Clin Transplant. 2013. PMID: 23432665
-
Rabbit antithymocyte globulin induction therapy in adult renal transplantation.Pharmacotherapy. 2006 Dec;26(12):1771-83. doi: 10.1592/phco.26.12.1771. Pharmacotherapy. 2006. PMID: 17125438 Review.
-
A review on comparing two commonly used rabbit anti-thymocyte globulins as induction therapy in solid organ transplantation.Expert Opin Biol Ther. 2013 Sep;13(9):1299-313. doi: 10.1517/14712598.2013.822064. Epub 2013 Jul 23. Expert Opin Biol Ther. 2013. PMID: 23875884 Review.
Cited by
-
Glycan microarray reveal induced IgGs repertoire shift against a dietary carbohydrate in response to rabbit anti-human thymocyte therapy.Oncotarget. 2017 Dec 11;8(68):112236-112244. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.23096. eCollection 2017 Dec 22. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 29348821 Free PMC article.
-
Challenging the Role of Diet-Induced Anti-Neu5Gc Antibodies in Human Pathologies.Front Immunol. 2020 Jun 9;11:834. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.00834. eCollection 2020. Front Immunol. 2020. PMID: 32655538 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Emerging Immunotherapies for Disease Modification of Type 1 Diabetes.Drugs. 2025 Apr;85(4):457-473. doi: 10.1007/s40265-025-02150-8. Epub 2025 Jan 28. Drugs. 2025. PMID: 39873914 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Induction therapy in kidney transplant recipients: Description of the practices according to the calendar period from the French multicentric DIVAT cohort.PLoS One. 2020 Oct 22;15(10):e0240929. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0240929. eCollection 2020. PLoS One. 2020. PMID: 33091057 Free PMC article.
-
Immune disguise: the mechanisms of Neu5Gc inducing autoimmune and transplant rejection.Genes Immun. 2022 Sep;23(6):175-182. doi: 10.1038/s41435-022-00182-8. Epub 2022 Sep 23. Genes Immun. 2022. PMID: 36151402 Review.
References
-
- Gaber LW, et al. Utility of standardized histological classification in the management of acute rejection. 1995 Efficacy Endpoints Conference. Transplantation. 1998;65(3):376–380. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

