TOGGLE: toolbox for generic NGS analyses
- PMID: 26552596
- PMCID: PMC4640241
- DOI: 10.1186/s12859-015-0795-6
TOGGLE: toolbox for generic NGS analyses
Abstract
Background: The explosion of NGS (Next Generation Sequencing) sequence data requires a huge effort in Bioinformatics methods and analyses. The creation of dedicated, robust and reliable pipelines able to handle dozens of samples from raw FASTQ data to relevant biological data is a time-consuming task in all projects relying on NGS. To address this, we created a generic and modular toolbox for developing such pipelines.
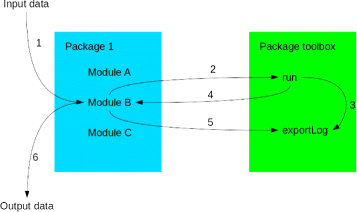
Results: TOGGLE (TOolbox for Generic nGs anaLysEs) is a suite of tools able to design pipelines that manage large sets of NGS softwares and utilities. Moreover, TOGGLE offers an easy way to manipulate the various options of the different softwares through the pipelines in using a single basic configuration file, which can be changed for each assay without having to change the code itself. We also describe one implementation of TOGGLE in a complete analysis pipeline designed for SNP discovery for large sets of genomic data, ready to use in different environments (from a single machine to HPC clusters).
Conclusion: TOGGLE speeds up the creation of robust pipelines with reliable log tracking and data flow, for a large range of analyses. Moreover, it enables Biologists to concentrate on the biological relevance of results, and change the experimental conditions easily. The whole code and test data are available at https://github.com/SouthGreenPlatform/TOGGLE .
Figures



References
-
- Kelly BJ, Fitch JR, Hu Y, Corsmeier DJ, Zhong H, Wetzel AN, et al. Churchill: an ultra-fast, deterministic, highly scalable and balanced parallelization strategy for the discovery of human genetic variation in clinical and population-scale genomics. Genome Biol. 2015;16(1):6. doi: 10.1186/s13059-014-0577-x. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

