In Vitro Activity of ASP2397 against Aspergillus Isolates with or without Acquired Azole Resistance Mechanisms
- PMID: 26552973
- PMCID: PMC4704222
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.02336-15
In Vitro Activity of ASP2397 against Aspergillus Isolates with or without Acquired Azole Resistance Mechanisms
Abstract
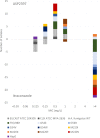
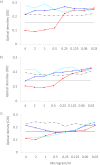
ASP2397 is a new compound with a novel and as-yet-unknown target different from that of licensed antifungal agents. It has activity against Aspergillus and Candida glabrata. We compared its in vitro activity against wild-type and azole-resistant A. fumigatus and A. terreus isolates with that of amphotericin B, itraconazole, posaconazole, and voriconazole. Thirty-four isolates, including 4 wild-type A. fumigatus isolates, 24 A. fumigatus isolates with alterations in CYP51A TR/L98H (5 isolates), M220 (9 isolates), G54 (9 isolates), and HapE (1 isolate), and A. terreus isolates (2 wild-type isolates and 1 isolate with an M217I CYP51A alteration), were analyzed. EUCAST E.Def 9.2 and CLSI M38-A2 MIC susceptibility testing was performed. ASP2397 MIC50 values (in milligrams per liter, with MIC ranges in parentheses) determined by EUCAST and CLSI were 0.5 (0.25 to 1) and 0.25 (0.06 to 0.25) against A. fumigatus CYP51A wild-type isolates and were similarly 0.5 (0.125 to >4) and 0.125 (0.06 to >4) against azole-resistant A. fumigatus isolates, respectively. These values were comparable to those for amphotericin B, which were 0.25 (0.125 to 0.5) and 0.25 (0.125 to 0.25) against wild-type isolates and 0.25 (0.125 to 1) and 0.25 (0.125 to 1) against isolates with azole resistance mechanisms, respectively. In contrast, MICs for the azole compounds were elevated and highest for itraconazole: >4 (1 to >4) and 4 (0.5 to >4) against isolates with azole resistance mechanisms compared to 0.125 (0.125 to 0.25) and 0.125 (0.06 to 0.25) against wild-type isolates, respectively. ASP2397 was active against A. terreus CYP51A wild-type isolates (MIC 0.5 to 1), whereas MICs of both azole and ASP2397 were elevated for the mutant isolate. ASP2397 displayed in vitro activity against A. fumigatus and A. terreus isolates which was independent of the presence or absence of azole target gene resistance mutations in A. fumigatus. The findings are promising at a time when azole-resistant A. fumigatus is emerging globally.
Copyright © 2015, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Herbrecht R, Denning DW, Patterson TF, Bennett JE, Greene RE, Oestmann J-W, Kern WV, Marr KA, Ribaud P, Lortholary O, Sylvester R, Rubin RH, Wingard JR, Stark P, Durand C, Caillot D, Thiel E, Chandrasekar PH, Hodges MR, Schlamm HT, Troke PF, de Pauw B. 2002. Voriconazole versus amphotericin B for primary therapy of invasive aspergillosis. N Engl J Med 347:408–415. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa020191. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Greene RE, Schlamm HT, Oestmann JW, Stark P, Durand C, Lortholary O, Wingard JR, Herbrecht R, Ribaud P, Patterson TF, Troke PF, Denning DW, Bennett JE, de Pauw BE, Rubin RH. 2007. Imaging findings in acute invasive pulmonary aspergillosis: clinical significance of the halo sign. Clin Infect Dis 44:373–379. doi:10.1086/509917. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Nivoix Y, Velten M, Letscher-Bru V, Moghaddam A, Natarajan-Amé S, Fohrer C, Lioure B, Bilger K, Lutun P, Marcellin L, Launoy A, Freys G, Bergerat J-P, Herbrecht R. 2008. Factors associated with overall and attributable mortality in invasive aspergillosis. Clin Infect Dis 47:1176–1184. doi:10.1086/592255. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Pagano L, Fianchi L, Fanci R, Candoni A, Caira M, Posteraro B, Morselli M, Valentini CG, Farina G, Mitra ME, Offidani M, Sanguinetti M, Tosti ME, Nosari A, Leone G, Viale P. 2010. Caspofungin for the treatment of candidaemia in patients with haematological malignancies. Clin Microbiol Infect 16:298–301. doi:10.1111/j.1469-0691.2009.02832.x. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

