Morphine-induced MOR-1X and ASF/SF2 Expressions Are Independent of Transcriptional Regulation: Implications for MOR-1X Signaling
- PMID: 26553431
- PMCID: PMC4801751
- DOI: 10.1002/jcp.25246
Morphine-induced MOR-1X and ASF/SF2 Expressions Are Independent of Transcriptional Regulation: Implications for MOR-1X Signaling
Abstract
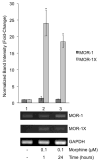
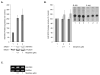
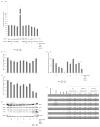
Recently, multiple μ-opioid receptor (MOR) isoforms have been identified that originate from a single gene, OPRM1; however, both their regulation and their functional significance are poorly characterized. The objectives of this study were to decipher, first, the regulation of alternatively spliced μ-opioid receptor isoforms and the spliceosome components that determine splicing specificity and, second, the signaling pathways utilized by particular isoforms both constitutively and following agonist binding. Our studies demonstrated that the expression of a particular splice variant, MOR-1X, was up-regulated by morphine, and this coincided with an increase in the essential splicing factor ASF/SF2. Structural comparison of this isoform to the prototypical variant MOR-1 revealed that the unique distal portion of the C-terminal domain contains additional phosphorylation sites, whereas functional comparison found distinct signaling differences, particularly in the ERK and p90 RSK pathways. Additionally, MOR-1X expression significantly reduced Bax expression and mitochondrial dehydrogenase activity, suggesting a unique functional consequence for MOR-1X specific signaling. Collectively, these findings suggest that alternative splicing of the MOR is altered by exogenous opioids, such as morphine, and that individual isoforms, such as MOR-1X, mediate unique signal transduction with distinct functional consequence. Furthermore, we have identified for the first time a potential mechanism that involves the essential splicing factor ASF/SF2 through which morphine regulates splicing specificity of the MOR encoding gene, OPRM1.
© 2015 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Figures
References
-
- Abbadie C, Pasternak GW. Opioid Receptors. Peptide Receptors. 2002;20:440.
-
- Ahn S, Shenoy SK, Wei H, Lefkowitz RJ. Differential kinetic and spatial patterns of beta-arrestin and G protein-mediated ERK activation by the angiotensin II receptor. The Journal of biological chemistry. 2004;279(34):35518–35525. - PubMed
-
- Anjum R, Blenis J. The RSK family of kinases: emerging roles in cellular signalling. Nature reviews Molecular cell biology. 2008;9(10):747–758. - PubMed
-
- Barki-Harrington L, Rockman HA. Beta-arrestins: multifunctional cellular mediators. Physiology (Bethesda) 2008;23:17–22. - PubMed
-
- Betito S, Cuvillier O. Regulation by sphingosine 1-phosphate of Bax and Bad activities during apoptosis in a MEK-dependent manner. Biochemical and biophysical research communications. 2006;340(4):1273–1277. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous