Combined Use of Oligopeptides, Fragment Libraries, and Natural Compounds: A Comprehensive Approach To Sample the Druggability of Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor
- PMID: 26553526
- PMCID: PMC5063151
- DOI: 10.1002/cmdc.201500467
Combined Use of Oligopeptides, Fragment Libraries, and Natural Compounds: A Comprehensive Approach To Sample the Druggability of Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor
Abstract
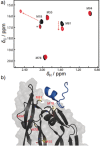
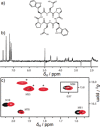
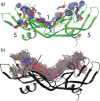
The modulation of protein-protein interactions (PPIs) is emerging as a highly promising tool to fight diseases. However, whereas an increasing number of compounds are able to disrupt peptide-mediated PPIs efficiently, the inhibition of domain-domain PPIs appears to be much more challenging. Herein, we report our results related to the interaction between vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) and its receptor (VEGFR). The VEGF-VEGFR interaction is a typical domain-domain PPI that is highly relevant for the treatment of cancer and some retinopathies. Our final goal was to identify ligands able to bind VEGF at the region used by the growth factor to interact with its receptor. We undertook an extensive study, combining a variety of experimental approaches, including NMR-spectroscopy-based screening of small organic fragments, peptide libraries, and medicinal plant extracts. The key feature of the successful ligands that emerged from this study was their capacity to expose hydrophobic functional groups able to interact with the hydrophobic hot spots at the interacting VEGF surface patch.
Keywords: drug discovery; fragment screening; growth factors; peptides; protein-protein interactions.
© 2015 The Authors. Published by Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Modulation, bioinformatic screening, and assessment of small molecular peptides targeting the vascular endothelial growth factor receptor.Cell Biochem Biophys. 2014 Dec;70(3):1913-21. doi: 10.1007/s12013-014-0151-x. Cell Biochem Biophys. 2014. PMID: 25069724 Free PMC article.
-
A novel peptide isolated from a phage display library inhibits tumor growth and metastasis by blocking the binding of vascular endothelial growth factor to its kinase domain receptor.J Biol Chem. 2002 Nov 8;277(45):43137-42. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M203103200. Epub 2002 Aug 14. J Biol Chem. 2002. PMID: 12183450
-
Anti-flt1 peptide, a vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 1-specific hexapeptide, inhibits tumor growth and metastasis.Clin Cancer Res. 2005 Apr 1;11(7):2651-61. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-04-1564. Clin Cancer Res. 2005. PMID: 15814646
-
Vascular endothelial cell growth factor (VEGF), an emerging target for cancer chemotherapy.Curr Med Chem Anticancer Agents. 2003 Mar;3(2):95-117. doi: 10.2174/1568011033353452. Curr Med Chem Anticancer Agents. 2003. PMID: 12678905 Review.
-
Antiangiogenic agents: an update on small molecule VEGFR inhibitors.Curr Med Chem. 2007;14(23):2495-516. doi: 10.2174/092986707782023622. Curr Med Chem. 2007. PMID: 17979703 Review.
Cited by
-
Peptide Inhibitors of Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor A: Current Situation and Perspectives.Pharmaceutics. 2021 Aug 26;13(9):1337. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics13091337. Pharmaceutics. 2021. PMID: 34575413 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Cyclic Peptide Epitope of an Under-Explored VEGF-B Loop 1 Demonstrated In Vivo Anti-Angiogenic and Anti-Tumor Activities.Front Pharmacol. 2021 Sep 29;12:734544. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.734544. eCollection 2021. Front Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 34658874 Free PMC article.
-
A Structural Overview of Vascular Endothelial Growth Factors Pharmacological Ligands: From Macromolecules to Designed Peptidomimetics.Molecules. 2021 Nov 9;26(22):6759. doi: 10.3390/molecules26226759. Molecules. 2021. PMID: 34833851 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Photoinduced reconfiguration to control the protein-binding affinity of azobenzene-cyclized peptides.J Mater Chem B. 2020 Aug 26;8(33):7413-7427. doi: 10.1039/d0tb01189d. J Mater Chem B. 2020. PMID: 32661544 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Han J. D., Dupuy D., Bertin N., Cusick M. E., Vidal M., Nat. Biotechnol. 2005, 23, 839–844. - PubMed
-
- Arkin M. R., Wells J. A., Nat. Rev. Drug Discovery 2004, 3, 301–317. - PubMed
-
- Nero T. L., Morton C. J., Holien J. K., Wielens J., Parker M. W., Nat. Rev. Cancer 2014, 14, 248–262. - PubMed
-
- Wells J. A., McClendon C. L., Nature 2007, 450, 1001–1009. - PubMed
-
- Hopkins A. L., Groom C. R., Nat. Rev. Drug Discovery 2002, 1, 727–730. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

