Natural killer cells in host defense against veterinary pathogens
- PMID: 26553564
- PMCID: PMC7112915
- DOI: 10.1016/j.vetimm.2015.10.001
Natural killer cells in host defense against veterinary pathogens
Abstract
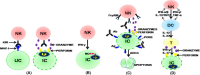
Natural Killer (NK) cells constitute a major subset of innate lymphoid cells that do not express the T- and B-cell receptors and play an important role in antimicrobial defense. NK cells not only induce early and rapid innate immune responses, but also communicate with dendritic cells to shape the adaptive immunity, thus bridging innate and adaptive immunity. Although the functional biology of NK cells is well-documented in a variety of infections in humans and mice, their role in protecting domestic animals from infectious agents is only beginning to be understood. In this article, we summarize the current state of knowledge about the contribution of NK cells in pathogen defense in domestic animals, especially cattle and pigs. Understanding the immunobiology of NK cells will translate into strategies to manipulate these cells for preventive and therapeutic purposes.
Keywords: Domestic animals; Immunity; Innate lymphoid cells; NK cells; Pathogens.
Copyright © 2015 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Differential recruitment and activation of natural killer cell sub-populations by Mycobacterium bovis-infected dendritic cells.Eur J Immunol. 2013 Jan;43(1):159-69. doi: 10.1002/eji.201242736. Epub 2012 Dec 3. Eur J Immunol. 2013. PMID: 23124835
-
Bovine natural killer cells.Vet Immunol Immunopathol. 2009 Aug 15;130(3-4):163-77. doi: 10.1016/j.vetimm.2009.02.017. Epub 2009 Mar 5. Vet Immunol Immunopathol. 2009. PMID: 19339058 Review.
-
Bovine natural killer cells acquire cytotoxic/effector activity following activation with IL-12/15 and reduce Mycobacterium bovis BCG in infected macrophages.J Leukoc Biol. 2006 Jan;79(1):71-9. doi: 10.1189/jlb.0505239. Epub 2005 Nov 7. J Leukoc Biol. 2006. PMID: 16275895
-
Roles of natural killer cells in antiviral immunity.Curr Opin Virol. 2016 Feb;16:15-23. doi: 10.1016/j.coviro.2015.10.008. Epub 2015 Nov 16. Curr Opin Virol. 2016. PMID: 26590692 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Viral Evasion of Natural Killer Cell Activation.Viruses. 2016 Apr 12;8(4):95. doi: 10.3390/v8040095. Viruses. 2016. PMID: 27077876 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
A Comprehensive Review of the Immunological Response against Foot-and-Mouth Disease Virus Infection and Its Evasion Mechanisms.Vaccines (Basel). 2020 Dec 14;8(4):764. doi: 10.3390/vaccines8040764. Vaccines (Basel). 2020. PMID: 33327628 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mucosal Immune System of Cattle: All Immune Responses Begin Here.Vet Clin North Am Food Anim Pract. 2019 Nov;35(3):431-451. doi: 10.1016/j.cvfa.2019.08.006. Vet Clin North Am Food Anim Pract. 2019. PMID: 31590896 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Semaphorin-3E Produced by Immature Dendritic Cells Regulates Activated Natural Killer Cells Migration.Front Immunol. 2018 May 9;9:1005. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.01005. eCollection 2018. Front Immunol. 2018. PMID: 29867980 Free PMC article.
-
Key Gaps in the Knowledge of the Porcine Respiratory Reproductive Syndrome Virus (PRRSV).Front Vet Sci. 2019 Feb 20;6:38. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2019.00038. eCollection 2019. Front Vet Sci. 2019. PMID: 30842948 Free PMC article. Review.
-
View Point: Semaphorin-3E: An Emerging Modulator of Natural Killer Cell Functions?Int J Mol Sci. 2017 Nov 5;18(11):2337. doi: 10.3390/ijms18112337. Int J Mol Sci. 2017. PMID: 29113093 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Artis D., Spits H. The biology of innate lymphoid cells. Nature. 2015;517:293–301. - PubMed
-
- Bastos R.G., Johnson W.C., Mwangi W., Brown W.C., Goff W.L. Bovine NK cells acquire cytotoxic activity and produce IFN-gamma after stimulation by Mycobacterium bovis BCG- or Babesia bovis-exposed splenic dendritic cells. Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 2008;124:302–312. - PubMed
-
- Bogdan C. Nitric oxide and the immune response. Nat. Immunol. 2001;2:907–916. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

