Population-Level Persistence of Immunity 2 Years After the PsA-TT Mass-Vaccination Campaign in Mali
- PMID: 26553687
- PMCID: PMC4639504
- DOI: 10.1093/cid/civ602
Population-Level Persistence of Immunity 2 Years After the PsA-TT Mass-Vaccination Campaign in Mali
Abstract
Background: In 2010, Africa's first preventive meningococcal mass vaccination campaign was launched using a newly developed Neisseria meningitidis group A (NmA) polysaccharide-tetanus toxoid conjugate vaccine, PsA-TT (MenAfriVac), designed specifically for the meningitis belt. Given PsA-TT's recent introduction, the duration of protection against meningococcal group A is unknown.
Methods: We conducted a household-based, age-stratified seroprevalence survey in Bamako, Mali, in 2012, 2 years after the vaccination campaign targeted all 1- to 29-year-olds. Randomly selected participants who had been eligible for PsA-TT provided a blood sample and responded to a questionnaire. Sera were analyzed to assess NmA-specific serum bactericidal antibody titers using rabbit complement (rSBA) and NmA-specific immunoglobulin G (IgG) by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. The proportion of participants putatively protected and the age group- and sex-specific rSBA geometric mean titers (GMTs) and IgG geometric mean concentrations (GMCs) were determined.
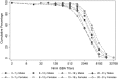
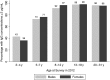
Results: Two years postvaccination, nearly all of the 800 participants (99.0%; 95% confidence interval [CI], 98.3%-99.7%) maintained NmA-specific rSBA titers ≥8, the accepted threshold for protection; 98.6% (95% CI, 97.8%-99.4%) had titers ≥128, and 89.5% (95% CI, 87.4%-91.6%) had titers ≥1024. The rSBA GMTs were significantly higher in females than in males aged <18 years at vaccination (P < .0001). NmA-specific IgG levels ≥2 µg/mL were found in 88.5% (95% CI, 86.3%-90.7%) of participants.
Conclusions: Two years after PsA-TT introduction, a very high proportion of the population targeted for vaccination maintains high antibody titers against NmA. Assessing the duration of protection provided by PsA-TT is a priority for implementing evidence-based vaccination strategies. Representative, population-based seroprevalence studies complement clinical trials and provide this key evidence.
Keywords: Africa; immunity; meningococcal vaccines; seroprevalence.
© The Author 2015. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the Infectious Diseases Society of America.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Higher Tetanus Toxoid Immunity 2 Years After PsA-TT Introduction in Mali.Clin Infect Dis. 2015 Nov 15;61 Suppl 5(Suppl 5):S578-85. doi: 10.1093/cid/civ513. Clin Infect Dis. 2015. PMID: 26553691 Free PMC article.
-
Meningococcal Seroepidemiology 1 Year After the PsA-TT Mass Immunization Campaign in Burkina Faso.Clin Infect Dis. 2015 Nov 15;61 Suppl 5(Suppl 5):S540-6. doi: 10.1093/cid/civ519. Clin Infect Dis. 2015. PMID: 26553686 Free PMC article.
-
Antibody Persistence at the Population Level 5 Years After Mass Vaccination With Meningococcal Serogroup A Conjugate Vaccine (PsA-TT) in Burkina Faso: Need for a Booster Campaign?Clin Infect Dis. 2019 Jan 18;68(3):435-443. doi: 10.1093/cid/ciy488. Clin Infect Dis. 2019. PMID: 30481265
-
Priorities for research on meningococcal disease and the impact of serogroup A vaccination in the African meningitis belt.Vaccine. 2013 Mar 1;31(11):1453-7. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2012.12.035. Epub 2012 Dec 27. Vaccine. 2013. PMID: 23273967 Free PMC article.
-
Group C meningococcal polysaccharide-tetanus toxoid conjugate vaccine: a meta-analysis of immunogenicity, safety and posology.Hum Vaccin. 2005 Jul-Aug;1(4):131-9. doi: 10.4161/hv.1.4.2018. Epub 2005 Jul 13. Hum Vaccin. 2005. PMID: 17012872 Review.
Cited by
-
Maternal immunisation with trivalent inactivated influenza vaccine for prevention of influenza in infants in Mali: a prospective, active-controlled, observer-blind, randomised phase 4 trial.Lancet Infect Dis. 2016 Sep;16(9):1026-1035. doi: 10.1016/S1473-3099(16)30054-8. Epub 2016 May 31. Lancet Infect Dis. 2016. PMID: 27261067 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Higher Tetanus Toxoid Immunity 2 Years After PsA-TT Introduction in Mali.Clin Infect Dis. 2015 Nov 15;61 Suppl 5(Suppl 5):S578-85. doi: 10.1093/cid/civ513. Clin Infect Dis. 2015. PMID: 26553691 Free PMC article.
References
-
- LaForce FM, Ravenscroft N, Djingarey M, Viviani S. Epidemic meningitis due to group A Neisseria meningitidis in the African meningitis belt: a persistent problem with an imminent solution. Vaccine 2009; 27(suppl 2):B13–9. - PubMed
-
- LaForce FM, Konde K, Viviani S, Preziosi MP. The Meningitis Vaccine Project. Vaccine 2007; 25(suppl 1):A97–100. - PubMed
-
- Jodar L, LaForce FM, Ceccarini C, Aguado T, Granoff DM. Meningococcal conjugate vaccine for Africa: a model for development of new vaccines for the poorest countries. Lancet 2003; 361:1902–4. - PubMed
-
- Okoko BJ, Idoko OT, Adegbola RA. Prospects and challenges with introduction of a mono-valent meningococcal conjugate vaccine in Africa. Vaccine 2009; 27:2023–9. - PubMed
-
- LaForce FM, Okwo-Bele JM. Eliminating epidemic group A meningococcal meningitis in Africa through a new vaccine. Health Affairs 2011; 30:1049–57. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

