Modeling Long-term Vaccination Strategies With MenAfriVac in the African Meningitis Belt
- PMID: 26553693
- PMCID: PMC4639487
- DOI: 10.1093/cid/civ508
Modeling Long-term Vaccination Strategies With MenAfriVac in the African Meningitis Belt
Abstract
Background: The introduction of MenAfriVac in campaigns targeting people aged 1-29 years across the African meningitis belt has successfully reduced meningitis incidence and carriage due to Neisseria meningitidis group A (MenA). It is important to consider how best to sustain population protection in the long term.
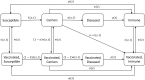
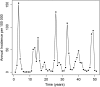
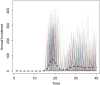
Methods: We created a mathematical model of MenA transmission and disease to investigate the potential impact of a range of immunization strategies. The model is age structured; includes classes of susceptible, carrier, ill, and immune people (who may be vaccinated or unvaccinated); and incorporates seasonal transmission and a stochastic forcing term that models between year variation in rates of transmission. Model parameters were primarily derived from African sources. The model can describe the typical annual incidence of meningitis in the prevaccine era, with irregular epidemics of varying size. Parameter and structural uncertainty were explored in sensitivity analyses.
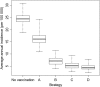
Results: Following MenAfriVac introduction at high uptake, the model predicts excellent short-term disease control. With no subsequent immunization, strong resurgences in disease incidence were predicted after approximately 15 years (assuming 10 years' average vaccine protection). Routine immunization at 9 months of age resulted in lower average annual incidence than regular mass campaigns of 1- to 4-year-olds, provided coverage was above approximately 60%. The strategy with the lowest overall average annual incidence and longest time to resurgence was achieved using a combination strategy of introduction into the Expanded Programme on Immunization at 9 months, 5 years after the initial mass campaigns, with a catch-up targeting unvaccinated 1- to 4-year-olds.
Conclusions: These results can be used to inform policy recommendations for long-term vaccination strategies with MenAfriVac.
Keywords: Africa; mathematical modeling; meningitis; vaccine.
© The Author 2015. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the Infectious Diseases Society of America.
Figures
References
-
- Frasch CE, Preziosi MP, LaForce FM. Development of a group A meningococcal conjugate vaccine, MenAfriVac(TM). Hum Vaccin Immunother 2012; 8:715–24. - PubMed
-
- Kristiansen PA, Diomande F, Ba AK et al. . Impact of the serogroup A meningococcal conjugate vaccine, MenAfriVac, on carriage and herd immunity. Clin Infect Dis 2013; 56:354–63. - PubMed
-
- Trotter CL, McVernon J, Ramsay ME et al. . Optimising the use of conjugate vaccines to prevent disease caused by Haemophilus influenzae type b, Neisseria meningitidis and Streptococcus pneumoniae. Vaccine 2008; 26:4434–45. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

