Accurate estimation of influenza epidemics using Google search data via ARGO
- PMID: 26553980
- PMCID: PMC4664296
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1515373112
Accurate estimation of influenza epidemics using Google search data via ARGO
Abstract
Accurate real-time tracking of influenza outbreaks helps public health officials make timely and meaningful decisions that could save lives. We propose an influenza tracking model, ARGO (AutoRegression with GOogle search data), that uses publicly available online search data. In addition to having a rigorous statistical foundation, ARGO outperforms all previously available Google-search-based tracking models, including the latest version of Google Flu Trends, even though it uses only low-quality search data as input from publicly available Google Trends and Google Correlate websites. ARGO not only incorporates the seasonality in influenza epidemics but also captures changes in people's online search behavior over time. ARGO is also flexible, self-correcting, robust, and scalable, making it a potentially powerful tool that can be used for real-time tracking of other social events at multiple temporal and spatial resolutions.
Keywords: autoregressive exogenous model; big data; digital disease detection; influenza-like illnesses activity real-time estimation; seasonal influenza.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
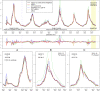
References
-
- Ginsberg J, et al. Detecting influenza epidemics using search engine query data. Nature. 2009;457(7232):1012–1014. - PubMed
-
- Polgreen PM, Chen Y, Pennock DM, Nelson FD, Weinstein RA. Using Internet searches for influenza surveillance. Clin Infect Dis. 2008;47(11):1443–1448. - PubMed
-
- Paul MJ, Dredze M, Broniatowski D. 2014. Twitter improves influenza forecasting. PLOS Curr Outbreaks 10.1371/currents.outbreaks.90b9ed0f59bae4ccaa683a39865d9117.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

