Implication of epithelial-mesenchymal transition in IGF1R-induced resistance to EGFR-TKIs in advanced non-small cell lung cancer
- PMID: 26554308
- PMCID: PMC4792560
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.6293
Implication of epithelial-mesenchymal transition in IGF1R-induced resistance to EGFR-TKIs in advanced non-small cell lung cancer
Abstract
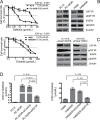
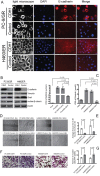
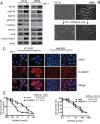
The underlying mechanisms for acquired resistance to epidermal growth factor receptor-tyrosine kinase inhibitors (EGFR-TKIs) in about 30%-40% of non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) patients remain elusive. Recent studies have suggested that activation of epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) and type 1 insulin-like growth factor receptor (IGF1R) is associated with acquired EGFR-TKIs resistance in NSCLC. Our study aims to further explore the mechanism of EMT and IGF1R in acquired EGFR-TKIs resistance in NSCLC cell lines with mutant (PC-9) or wild-type EGFR (H460). Compared to parental cells, EGFR-TKIs-resistant PC-9/GR and H460/ER cells displayed an EMT phenotype and showed overexpression of IGF1R. SiIGF1R in PC-9/GR and H460/ER cells reversed EMT-related morphologies and reversed their resistance to EGFR-TKIs. Exogenous IGF-1 alone induced EMT in EGFR-TKIs-naïve PC-9 and H460 cells and increased their resistance against EGFR-TKIs. Inducing EMT by TGF-β1 in PC-9 and H460 cells decreased their sensitivity to EGFR-TKIs, whereas reversing EMT by E-cadherin overexpression in PC-9/GR and H460/ER cells restored their sensitivity to EGFR-TKIs. These data suggest that IGF1R plays an important role in acquired drug resistance against EGFR-TKIs by inducing EMT. Targeting IGF1R and EMT may be a potential therapeutic strategy for advanced NSCLC with acquired EGFR-TKIs resistance.
Keywords: drug resistance; epidermal growth factor receptor-tyrosine kinase inhibitors; epithelial-mesenchymal transition; non-small cell lung cancer; type 1 insulin-like growth factor receptor.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Notch-1 contributes to epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor acquired resistance in non-small cell lung cancer in vitro and in vivo.Eur J Cancer. 2013 Nov;49(16):3559-72. doi: 10.1016/j.ejca.2013.07.007. Epub 2013 Aug 2. Eur J Cancer. 2013. PMID: 23916913
-
Bidirectional signaling between TM4SF5 and IGF1R promotes resistance to EGFR kinase inhibitors.Lung Cancer. 2015 Oct;90(1):22-31. doi: 10.1016/j.lungcan.2015.06.023. Epub 2015 Jul 2. Lung Cancer. 2015. PMID: 26190015
-
Sensitivity to chemotherapeutics of NSCLC cells with acquired resistance to EGFR-TKIs is mediated by T790M mutation or epithelial-mesenchymal transition.Oncol Rep. 2018 Apr;39(4):1783-1792. doi: 10.3892/or.2018.6242. Epub 2018 Feb 1. Oncol Rep. 2018. PMID: 29393480
-
Current mechanism of acquired resistance to epidermal growth factor receptor-tyrosine kinase inhibitors and updated therapy strategies in human nonsmall cell lung cancer.J Cancer Res Ther. 2016 Dec;12(Supplement):C131-C137. doi: 10.4103/0973-1482.200613. J Cancer Res Ther. 2016. PMID: 28230005 Review.
-
Acquired resistance of non-small cell lung cancer to epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors.Respir Investig. 2014 Mar;52(2):82-91. doi: 10.1016/j.resinv.2013.07.007. Epub 2013 Aug 30. Respir Investig. 2014. PMID: 24636263 Review.
Cited by
-
Exosome-derived miR-210 involved in resistance to osimertinib and epithelial-mesenchymal transition in EGFR mutant non-small cell lung cancer cells.Thorac Cancer. 2021 Jun;12(11):1690-1698. doi: 10.1111/1759-7714.13943. Epub 2021 May 3. Thorac Cancer. 2021. PMID: 33939301 Free PMC article.
-
Combination Strategies Using EGFR-TKi in NSCLC Therapy: Learning from the Gap between Pre-Clinical Results and Clinical Outcomes.Int J Biol Sci. 2018 Feb 5;14(2):204-216. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.22955. eCollection 2018. Int J Biol Sci. 2018. PMID: 29483838 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Glycans as Regulatory Elements of the Insulin/IGF System: Impact in Cancer Progression.Int J Mol Sci. 2017 Sep 7;18(9):1921. doi: 10.3390/ijms18091921. Int J Mol Sci. 2017. PMID: 28880250 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Molecular Targets in Lung Cancer: Study of the Evolution of Biomarkers Associated with Treatment with Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors-Has NF1 Tumor Suppressor a Key Role in Acquired Resistance?Cancers (Basel). 2022 Jul 7;14(14):3323. doi: 10.3390/cancers14143323. Cancers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35884384 Free PMC article.
-
Intrinsic resistance to EGFR-Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors in EGFR-Mutant Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: Differences and Similarities with Acquired Resistance.Cancers (Basel). 2019 Jul 1;11(7):923. doi: 10.3390/cancers11070923. Cancers (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31266248 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Perez-Soler R, Chachoua A, Hammond LA, Rowinsky EK, Huberman M, Karp D, Rigas J, Clark GM, Santabarbara P, Bonomi P. Determinants of tumor response and survival with erlotinib in patients with non--small-cell lung cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2004;22:3238–3247. - PubMed
-
- Riely GJ, Pao W, Pham D, Li AR, Rizvi N, Venkatraman ES, Zakowski MF, Kris MG, Ladanyi M, Miller VA. Clinical course of patients with non-small cell lung cancer and epidermal growth factor receptor exon 19 and exon 21 mutations treated with gefitinib or erlotinib. Clin Cancer Res. 2006;12:839–844. - PubMed
-
- Sequist LV, Waltman BA, Dias-Santagata D, Digumarthy S, Turke AB, Fidias P, Bergethon K, Shaw AT, Gettinger S, Cosper AK, Akhavanfard S, Heist RS, Temel J, et al. Genotypic and histological evolution of lung cancers acquiring resistance to EGFR inhibitors. Sci Transl Med. 2011;3:26r–75r. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Kobayashi S, Boggon TJ, Dayaram T, Janne PA, Kocher O, Meyerson M, Johnson BE, Eck MJ, Tenen DG, Halmos B. EGFR mutation and resistance of non-small-cell lung cancer to gefitinib. N Engl J Med. 2005;352:786–792. - PubMed
-
- Shih JY, Gow CH, Yang PC. EGFR mutation conferring primary resistance to gefitinib in non-small-cell lung cancer. N Engl J Med. 2005;353:207–208. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

