p21-activated kinase group II small compound inhibitor GNE-2861 perturbs estrogen receptor alpha signaling and restores tamoxifen-sensitivity in breast cancer cells
- PMID: 26554417
- PMCID: PMC4791272
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.6081
p21-activated kinase group II small compound inhibitor GNE-2861 perturbs estrogen receptor alpha signaling and restores tamoxifen-sensitivity in breast cancer cells
Abstract
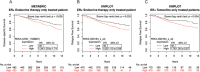
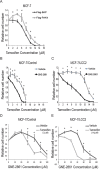
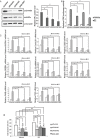
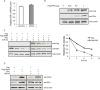
Estrogen receptor alpha (ERα) is highly expressed in most breast cancers. Consequently, ERα modulators, such as tamoxifen, are successful in breast cancer treatment, although tamoxifen resistance is commonly observed. While tamoxifen resistance may be caused by altered ERα signaling, the molecular mechanisms regulating ERα signaling and tamoxifen resistance are not entirely clear. Here, we found that PAK4 expression was consistently correlated to poor patient outcome in endocrine treated and tamoxifen-only treated breast cancer patients. Importantly, while PAK4 overexpression promoted tamoxifen resistance in MCF-7 human breast cancer cells, pharmacological treatment with a group II PAK (PAK4, 5, 6) inhibitor, GNE-2861, sensitized tamoxifen resistant MCF-7/LCC2 breast cancer cells to tamoxifen. Mechanistically, we identified a regulatory positive feedback loop, where ERα bound to the PAK4 gene, thereby promoting PAK4 expression, while PAK4 in turn stabilized the ERα protein, activated ERα transcriptional activity and ERα target gene expression. Further, PAK4 phosphorylated ERα-Ser305, a phosphorylation event needed for the PAK4 activation of ERα-dependent transcription. In conclusion, PAK4 may be a suitable target for perturbing ERα signaling and tamoxifen resistance in breast cancer patients.
Keywords: ERα; PAK4; phosphorylation; small molecule inhibitor; tamoxifen resistance.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Loss of Rho GDIα and resistance to tamoxifen via effects on estrogen receptor α.J Natl Cancer Inst. 2011 Apr 6;103(7):538-52. doi: 10.1093/jnci/djr058. Epub 2011 Mar 29. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2011. PMID: 21447808 Free PMC article.
-
MiRNA-27a sensitizes breast cancer cells to treatment with Selective Estrogen Receptor Modulators.Breast. 2019 Feb;43:31-38. doi: 10.1016/j.breast.2018.10.007. Epub 2018 Oct 18. Breast. 2019. PMID: 30415143
-
Estrogen receptor α is the major driving factor for growth in tamoxifen-resistant breast cancer and supported by HER/ERK signaling.Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2013 May;139(1):71-80. doi: 10.1007/s10549-013-2485-2. Epub 2013 Apr 23. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2013. PMID: 23609470
-
Stemness Phenotype in Tamoxifen Resistant Breast Cancer Cells May be Induced by Interactions Between Receptor Tyrosine Kinases and ERα-66.Recent Pat Anticancer Drug Discov. 2018;13(3):302-307. doi: 10.2174/1574892813666180305164634. Recent Pat Anticancer Drug Discov. 2018. PMID: 29512469 Review.
-
Clinical significance of estrogen receptor phosphorylation.Endocr Relat Cancer. 2011 Jan 19;18(1):R1-14. doi: 10.1677/ERC-10-0070. Print 2011 Feb. Endocr Relat Cancer. 2011. PMID: 21149515 Review.
Cited by
-
Inhibition of NAMPT by PAK4 Inhibitors.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Sep 21;25(18):10138. doi: 10.3390/ijms251810138. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39337621 Free PMC article.
-
Dissecting the Roles of PDCD4 in Breast Cancer.Front Oncol. 2022 Jun 20;12:855807. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.855807. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35795053 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Heat*seq: an interactive web tool for high-throughput sequencing experiment comparison with public data.Bioinformatics. 2016 Nov 1;32(21):3354-3356. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btw407. Epub 2016 Jul 4. Bioinformatics. 2016. PMID: 27378302 Free PMC article.
-
STAT1 facilitates oestrogen receptor α transcription and stimulates breast cancer cell proliferation.J Cell Mol Med. 2018 Dec;22(12):6077-6086. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.13882. Epub 2018 Oct 17. J Cell Mol Med. 2018. PMID: 30334368 Free PMC article.
-
A mandatory role of nuclear PAK4-LIFR axis in breast-to-bone metastasis of ERα-positive breast cancer cells.Oncogene. 2019 Feb;38(6):808-821. doi: 10.1038/s41388-018-0456-0. Epub 2018 Sep 3. Oncogene. 2019. PMID: 30177834 Free PMC article.
References
-
- DeSantis C, Ma J, Bryan L, Jemal A. Breast cancer statistics, 2013. CA: a cancer journal for clinicians. 2014;64:52–62. - PubMed
-
- Jakesz R, Smith CA, Aitken S, Huff K, Schuette W, Shackney S, Lippman M. Influence of cell proliferation and cell cycle phase on expression of estrogen receptor in MCF-7 breast cancer cells. Cancer research. 1984;44:619–625. - PubMed
-
- Lin CY, Strom A, Vega VB, Kong SL, Yeo AL, Thomsen JS, Chan WC, Doray B, Bangarusamy DK, Ramasamy A, Vergara LA, Tang S, Chong A, Bajic VB, Miller LD, Gustafsson JA, et al. Discovery of estrogen receptor alpha target genes and response elements in breast tumor cells. Genome biology. 2004;5:R66. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Clarke R, Leonessa F, Welch JN, Skaar TC. Cellular and molecular pharmacology of antiestrogen action and resistance. Pharmacological reviews. 2001;53:25–71. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

