Submaximal cardiopulmonary thresholds on a robotics-assisted tilt table, a cycle and a treadmill: a comparative analysis
- PMID: 26555762
- PMCID: PMC4641341
- DOI: 10.1186/s12938-015-0099-0
Submaximal cardiopulmonary thresholds on a robotics-assisted tilt table, a cycle and a treadmill: a comparative analysis
Abstract
Background: The robotics-assisted tilt table (RATT), including actuators for tilting and cyclical leg movement, is used for rehabilitation of severely disabled neurological patients. Following further engineering development of the system, i.e. the addition of force sensors and visual bio-feedback, patients can actively participate in exercise testing and training on the device. Peak cardiopulmonary performance parameters were previously investigated, but it also important to compare submaximal parameters with standard devices. The aim of this study was to evaluate the feasibility of the RATT for estimation of submaximal exercise thresholds by comparison with a cycle ergometer and a treadmill.
Methods: 17 healthy subjects randomly performed six maximal individualized incremental exercise tests, with two tests on each of the three exercise modalities. The ventilatory anaerobic threshold (VAT) and respiratory compensation point (RCP) were determined from breath-by-breath data.
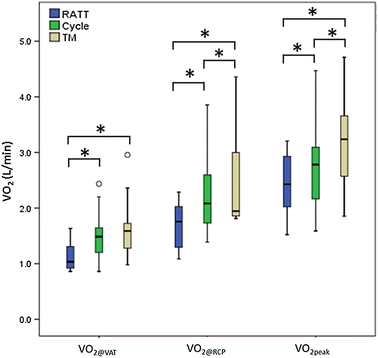
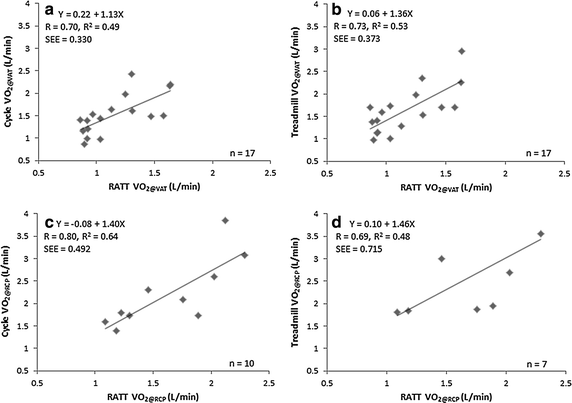
Results: VAT and RCP on the RATT were lower than the cycle ergometer and the treadmill: oxygen uptake (V'O2) at VAT was [mean (SD)] 1.2 (0.3), 1.5 (0.4) and 1.6 (0.5) L/min, respectively (p < 0.001); V'O2 at RCP was 1.7 (0.4), 2.3 (0.8) and 2.6 (0.9) L/min, respectively (p = 0.001). High correlations for VAT and RCP were found between the RATT vs the cycle ergometer and RATT vs the treadmill (R on the range 0.69-0.80). VAT and RCP demonstrated excellent test-retest reliability for all three devices (ICC from 0.81 to 0.98). Mean differences between the test and retest values on each device were close to zero. The ventilatory equivalent for O2 at VAT for the RATT and cycle ergometer were similar and both were higher than the treadmill. The ventilatory equivalent for CO2 at RCP was similar for all devices. Ventilatory equivalent parameters demonstrated fair-to-excellent reliability and repeatability.
Conclusions: It is feasible to use the RATT for estimation of submaximal exercise thresholds: VAT and RCP on the RATT were lower than the cycle ergometer and the treadmill, but there were high correlations between the RATT vs the cycle ergometer and vs the treadmill. Repeatability and test-retest reliability of all submaximal threshold parameters from the RATT were comparable to those of standard devices.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Test-retest reliability and four-week changes in cardiopulmonary fitness in stroke patients: evaluation using a robotics-assisted tilt table.BMC Neurol. 2016 Sep 6;16(1):163. doi: 10.1186/s12883-016-0686-0. BMC Neurol. 2016. PMID: 27600918 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of peak cardiopulmonary performance parameters on a robotics-assisted tilt table, a cycle and a treadmill.PLoS One. 2015 Apr 10;10(4):e0122767. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0122767. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 25860019 Free PMC article.
-
Feasibility of cardiopulmonary exercise testing and training using a robotics-assisted tilt table in dependent-ambulatory stroke patients.J Neuroeng Rehabil. 2015 Sep 26;12:88. doi: 10.1186/s12984-015-0078-5. J Neuroeng Rehabil. 2015. PMID: 26410821 Free PMC article.
-
Physiological rationale of commonly used clinical exercise tests.Pulmonology. 2020 May-Jun;26(3):159-165. doi: 10.1016/j.pulmoe.2019.10.004. Epub 2020 Apr 4. Pulmonology. 2020. PMID: 32265152 Review.
-
Gas exchange during exercise in obese children.Eur J Pediatr. 1989 Jun;148(7):614-7. doi: 10.1007/BF00441512. Eur J Pediatr. 1989. PMID: 2663513 Review.
Cited by
-
Changes in heart rate variability at rest and during exercise in patients after a stroke: a feasibility study.Biomed Eng Online. 2024 Dec 26;23(1):132. doi: 10.1186/s12938-024-01328-7. Biomed Eng Online. 2024. PMID: 39726043 Free PMC article.
-
Test-retest reliability and four-week changes in cardiopulmonary fitness in stroke patients: evaluation using a robotics-assisted tilt table.BMC Neurol. 2016 Sep 6;16(1):163. doi: 10.1186/s12883-016-0686-0. BMC Neurol. 2016. PMID: 27600918 Free PMC article.
-
Ventilatory efficiency during constant-load test at lactate threshold intensity: Endurance versus resistance exercises.PLoS One. 2019 May 21;14(5):e0216824. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0216824. eCollection 2019. PLoS One. 2019. PMID: 31112561 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Similar Slow Component of Oxygen Uptake and Ventilatory Efficiency between an Aerobic Dance Session on an Air Dissipation Platform and a Constant-Load Treadmill Test in Healthy Women.Biology (Basel). 2022 Nov 10;11(11):1646. doi: 10.3390/biology11111646. Biology (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36358347 Free PMC article.
-
Investigation of cardiopulmonary exercise testing using a dynamic leg press and comparison with a cycle ergometer.BMC Sports Sci Med Rehabil. 2018 Feb 15;10:5. doi: 10.1186/s13102-018-0095-3. eCollection 2018. BMC Sports Sci Med Rehabil. 2018. PMID: 29468072 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bichsel L, Sommer M, Hunt KJ. Development of a biofeedback system for controlling the patients work rate, heart rate and oxygen uptake during robot-assisted tilt table therapy. Automatisierungstechnik. 2011;59:622–628. doi: 10.1524/auto.2011.0953. - DOI
-
- Laubacher M, Perret C, Hunt KJ. Work-rate-guided exercise testing in patients with incomplete spinal cord injury using a robotics-assisted tilt-table. Disabil Rehabil Assist Technol. 2015;10:433–438. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

