Hemodynamic Surveillance of Ventricular Pacing Effectiveness with the Transvalvular Impedance Sensor
- PMID: 26556408
- PMCID: PMC4590946
- DOI: 10.1155/2014/307168
Hemodynamic Surveillance of Ventricular Pacing Effectiveness with the Transvalvular Impedance Sensor
Abstract
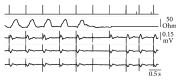
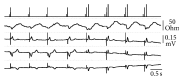
The Transvalvular Impedance (TVI) is derived between atrial and ventricular pacing electrodes. A sharp TVI increase in systole is an ejection marker, allowing the hemodynamic surveillance of ventricular stimulation effectiveness in pacemaker patients. At routine follow-up checks, the ventricular threshold test was managed by the stimulator with the supervision of a physician, who monitored the surface ECG. When the energy scan resulted in capture loss, the TVI system must detect the failure and increase the output voltage. A TVI signal suitable to this purpose was present in 85% of the tested patients. A total of 230 capture failures, induced in 115 patients in both supine and sitting upright positions, were all promptly recognized by real-time TVI analysis (100% sensitivity). The procedure was never interrupted by the physician, as the automatic energy regulation ensured full patient's safety. The pulse energy was then set at 4 times the threshold to test the alarm specificity during daily activity (sitting, standing up, and walking). The median prevalence of false alarms was 0.336%. The study shows that TVI-based ejection assessment is a valuable approach to the verification of pacing reliability and the autoregulation of ventricular stimulation energy.
Figures

References
-
- Biffi M., Sperzel J., Martignani C., Branzi A., Boriani G. Evolution of pacing for bradycardia: autocapture. European Heart Journal, Supplement. 2007;9:I23–I32. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/sum058. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

