PH Domain-Arf G Protein Interactions Localize the Arf-GEF Steppke for Cleavage Furrow Regulation in Drosophila
- PMID: 26556630
- PMCID: PMC4640550
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0142562
PH Domain-Arf G Protein Interactions Localize the Arf-GEF Steppke for Cleavage Furrow Regulation in Drosophila
Abstract
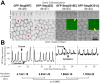
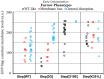
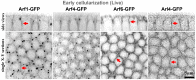
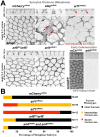
The recruitment of GDP/GTP exchange factors (GEFs) to specific subcellular sites dictates where they activate small G proteins for the regulation of various cellular processes. Cytohesins are a conserved family of plasma membrane GEFs for Arf small G proteins that regulate endocytosis. Analyses of mammalian cytohesins have identified a number of recruitment mechanisms for these multi-domain proteins, but the conservation and developmental roles for these mechanisms are unclear. Here, we report how the pleckstrin homology (PH) domain of the Drosophila cytohesin Steppke affects its localization and activity at cleavage furrows of the early embryo. We found that the PH domain is necessary for Steppke furrow localization, and for it to regulate furrow structure. However, the PH domain was not sufficient for the localization. Next, we examined the role of conserved PH domain amino acid residues that are required for mammalian cytohesins to bind PIP3 or GTP-bound Arf G proteins. We confirmed that the Steppke PH domain preferentially binds PIP3 in vitro through a conserved mechanism. However, disruption of residues for PIP3 binding had no apparent effect on GFP-Steppke localization and effects. Rather, residues for binding to GTP-bound Arf G proteins made major contributions to this Steppke localization and activity. By analyzing GFP-tagged Arf and Arf-like small G proteins, we found that Arf1-GFP, Arf6-GFP and Arl4-GFP, but not Arf4-GFP, localized to furrows. However, analyses of embryos depleted of Arf1, Arf6 or Arl4 revealed either earlier defects than occur in embryos depleted of Steppke, or no detectable furrow defects, possibly because of redundancies, and thus it was difficult to assess how individual Arf small G proteins affect Steppke. Nonetheless, our data show that the Steppke PH domain and its conserved residues for binding to GTP-bound Arf G proteins have substantial effects on Steppke localization and activity in early Drosophila embryos.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



Similar articles
-
Stepping stone: a cytohesin adaptor for membrane cytoskeleton restraint in the syncytial Drosophila embryo.Mol Biol Cell. 2015 Feb 15;26(4):711-25. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E14-11-1554. Epub 2014 Dec 24. Mol Biol Cell. 2015. PMID: 25540427 Free PMC article.
-
The Arf GAP Asap promotes Arf1 function at the Golgi for cleavage furrow biosynthesis in Drosophila.Mol Biol Cell. 2016 Oct 15;27(20):3143-3155. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E16-05-0272. Epub 2016 Aug 17. Mol Biol Cell. 2016. PMID: 27535433 Free PMC article.
-
An Arf-GEF regulates antagonism between endocytosis and the cytoskeleton for Drosophila blastoderm development.Curr Biol. 2013 Nov 4;23(21):2110-20. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2013.08.058. Epub 2013 Oct 10. Curr Biol. 2013. PMID: 24120639
-
Localization and function of Arf family GTPases.Biochem Soc Trans. 2005 Aug;33(Pt 4):639-42. doi: 10.1042/BST0330639. Biochem Soc Trans. 2005. PMID: 16042562 Review.
-
The role of ADP-ribosylation factor and SAR1 in vesicular trafficking in plants.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2004 Jul 1;1664(1):9-30. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamem.2004.04.005. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2004. PMID: 15238254 Review.
Cited by
-
Membrane-actin interactions in morphogenesis: Lessons learned from Drosophila cellularization.Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2023 Jan 15;133:107-122. doi: 10.1016/j.semcdb.2022.03.028. Epub 2022 Apr 5. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2023. PMID: 35396167 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dysregulation of the endoplasmic reticulum blocks recruitment of centrosome-associated proteins resulting in mitotic failure.Development. 2023 Nov 15;150(22):dev201917. doi: 10.1242/dev.201917. Epub 2023 Nov 17. Development. 2023. PMID: 37971218 Free PMC article.
-
In vivo Functional Genomics for Undiagnosed Patients: The Impact of Small GTPases Signaling Dysregulation at Pan-Embryo Developmental Scale.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021 May 25;9:642235. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.642235. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021. PMID: 34124035 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Key roles of Arf small G proteins and biosynthetic trafficking for animal development.Small GTPases. 2019 Nov;10(6):403-410. doi: 10.1080/21541248.2017.1304854. Epub 2017 Apr 17. Small GTPases. 2019. PMID: 28410007 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A phosphate-sensing organelle regulates phosphate and tissue homeostasis.Nature. 2023 May;617(7962):798-806. doi: 10.1038/s41586-023-06039-y. Epub 2023 May 3. Nature. 2023. PMID: 37138087 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

