Leptin as a mediator of tumor-stromal interactions promotes breast cancer stem cell activity
- PMID: 26556856
- PMCID: PMC4811458
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.6014
Leptin as a mediator of tumor-stromal interactions promotes breast cancer stem cell activity
Abstract
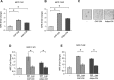
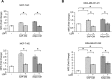
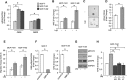
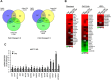
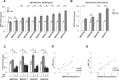
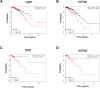
Breast cancer stem cells (BCSCs) play crucial roles in tumor initiation, metastasis and therapeutic resistance. A strict dependency between BCSCs and stromal cell components of tumor microenvironment exists. Thus, novel therapeutic strategies aimed to target the crosstalk between activated microenvironment and BCSCs have the potential to improve clinical outcome. Here, we investigated how leptin, as a mediator of tumor-stromal interactions, may affect BCSC activity using patient-derived samples (n = 16) and breast cancer cell lines, and determined the potential benefit of targeting leptin signaling in these model systems. Conditioned media (CM) from cancer-associated fibroblasts and breast adipocytes significantly increased mammosphere formation in breast cancer cells and depletion of leptin from CM completely abrogated this effect. Mammosphere cultures exhibited increased leptin receptor (OBR) expression and leptin exposure enhanced mammosphere formation. Microarray analyses revealed a similar expression profile of genes involved in stem cell biology among mammospheres treated with CM and leptin. Interestingly, leptin increased mammosphere formation in metastatic breast cancers and expression of OBR as well as HSP90, a target of leptin signaling, were directly correlated with mammosphere formation in metastatic samples (r = 0.68/p = 0.05; r = 0.71/p = 0.036, respectively). Kaplan-Meier survival curves indicated that OBR and HSP90 expression were associated with reduced overall survival in breast cancer patients (HR = 1.9/p = 0.022; HR = 2.2/p = 0.00017, respectively). Furthermore, blocking leptin signaling by using a full leptin receptor antagonist significantly reduced mammosphere formation in breast cancer cell lines and patient-derived samples. Our results suggest that leptin/leptin receptor signaling may represent a potential therapeutic target that can block the stromal-tumor interactions driving BCSC-mediated disease progression.
Keywords: CAFs; breast cancer; breast cancer stem cells; leptin; microenvironment.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Jemal A, Siegel R, Xu J, Ward E. Cancer statistics, 2010. CA Cancer J Clin. 2010;60:277–300. - PubMed
-
- Visvader JE, Lindeman GJ. Cancer stem cells in solid tumours: accumulating evidence and unresolved questions. Nat Rev Cancer. 2008;8:755–768. - PubMed
-
- Clarke MF, Dick JE, Dirks PB, Eaves CJ, Jamieson CH, Jones DL, Visvader J, Weissman IL, Wahl GM. Cancer stem cells—perspectives on current status and future directions: AACR Workshop on cancer stem cells. Cancer Res. 2006;66:9339–9344. - PubMed
-
- Li X, Lewis MT, Huang J, Gutierrez C, Osborne CK, Wu MF, Hilsenbeck SG, Pavlick A, Zhang X, Chamness GC, Wong H, Rosen J, Chang JC. Intrinsic resistance of tumorigenic breast cancer cells to chemotherapy. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2008;100:672–679. - PubMed
-
- Phillips TM, McBride WH, Pajonk F. The response of CD24(-/low)/CD44+ breast cancer-initiating cells to radiation. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2006;98:1777–1785. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

