Inflammation: A novel target of current therapies for hepatic encephalopathy in liver cirrhosis
- PMID: 26557005
- PMCID: PMC4631979
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i41.11815
Inflammation: A novel target of current therapies for hepatic encephalopathy in liver cirrhosis
Abstract
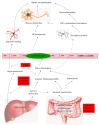
Hepatic encephalopathy (HE) is a severe neuropsychiatric syndrome that most commonly occurs in decompensated liver cirrhosis and incorporates a spectrum of manifestations that ranges from mild cognitive impairment to coma. Although the etiology of HE is not completely understood, it is believed that multiple underlying mechanisms are involved in the pathogenesis of HE, and one of the main factors is thought to be ammonia; however, the ammonia hypothesis in the pathogenesis of HE is incomplete. Recently, it has been increasingly demonstrated that inflammation, including systemic inflammation, neuroinflammation and endotoxemia, acts in concert with ammonia in the pathogenesis of HE in cirrhotic patients. Meanwhile, a good number of studies have found that current therapies for HE, such as lactulose, rifaximin, probiotics and the molecular adsorbent recirculating system, could inhibit different types of inflammation, thereby improving the neuropsychiatric manifestations and preventing the progression of HE in cirrhotic patients. The anti-inflammatory effects of these current therapies provide a novel therapeutic approach for cirrhotic patients with HE. The purpose of this review is to describe the inflammatory mechanisms behind the etiology of HE in cirrhosis and discuss the current therapies that target the inflammatory pathogenesis of HE.
Keywords: Hepatic encephalopathy; Inflammation; Pathogenesis; Treatment.
Figures
References
-
- Vilstrup H, Amodio P, Bajaj J, Cordoba J, Ferenci P, Mullen KD, Weissenborn K, Wong P. Hepatic encephalopathy in chronic liver disease: 2014 Practice Guideline by the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases and the European Association for the Study of the Liver. Hepatology. 2014;60:715–735. - PubMed
-
- Ortiz M, Jacas C, Córdoba J. Minimal hepatic encephalopathy: diagnosis, clinical significance and recommendations. J Hepatol. 2005;42 Suppl:S45–S53. - PubMed
-
- Prasad S, Dhiman RK, Duseja A, Chawla YK, Sharma A, Agarwal R. Lactulose improves cognitive functions and health-related quality of life in patients with cirrhosis who have minimal hepatic encephalopathy. Hepatology. 2007;45:549–559. - PubMed
-
- Bajaj JS, Saeian K, Verber MD, Hischke D, Hoffmann RG, Franco J, Varma RR, Rao SM. Inhibitory control test is a simple method to diagnose minimal hepatic encephalopathy and predict development of overt hepatic encephalopathy. Am J Gastroenterol. 2007;102:754–760. - PubMed
-
- Castro-Tavares J. Effects of isoprenaline and phenylephrine on plasma potassium: role of the liver. Arch Int Pharmacodyn Ther. 1975;218:110–119. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

