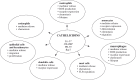
Cathelicidin impact on inflammatory cells
- PMID: 26557038
- PMCID: PMC4637384
- DOI: 10.5114/ceji.2015.51359
Cathelicidin impact on inflammatory cells
Abstract
Cathelicidins, like other antimicrobial peptides, exhibit direct antimicrobial activities against a broad spectrum of microbes, including both Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria, enveloped viruses, and fungi. These host-derived peptides kill the invaded pathogens by perturbing their cell membranes and can neutralize biological activities of endotoxin. Nowadays, more and more data indicate that these peptides, in addition to their antimicrobial properties, possess various immunomodulatory activities. Cathelicidins have the potential to influence and modulate, both directly and indirectly, the activity of various cell populations involved in inflammatory processes and in host defense against invading pathogens. They induce migration of neutrophils, monocytes/macrophages, eosinophils, and mast cells and prolong the lifespan of neutrophils. These peptides directly activate inflammatory cells to production and release of different pro-inflammatory and immunoregulatory mediators, cytokines, and chemokines, however cathelicidins might mediate the generation of anti-inflammatory cytokines as well. Cathelicidins also modulate epithelial cell/keratinocyte responses to infecting pathogens. What is more, they affect activity of monocytes, dendritic cells, keratinocytes, or epithelial cells acting in synergy with cytokines or β-defensins. In addition, these peptides indirectly balance TLR-mediated responses of monocytes, macrophages, dendritic cells, epithelial cells, and keratinocytes. This review discusses the role and significance of cathelicidins in inflammation and innate immunity against pathogens.
Keywords: cathelicidins; inflammation; innate immunity; macrophages; mast cells; monocytes; neutrophils.
Figures
References
-
- Barlow PG, Findlay EG, Currie SM, Davidson DJ. Antiviral potential of cathelicidins. Future Microbiol. 2014;9:55–73. - PubMed
-
- Mansour SC, Pena OM, Hancock RE. Host defense peptides: front-line immunomodulators. Trends Immun. 2014;35:443–450. - PubMed
-
- Guani-Guerra E, Santos-Mendoza T, Lugo-Reyes SO, Téra LM. Antimicrobial peptides: general overview and clinical implications in human health and disease. Clin Immunol. 2010;135:1–11. - PubMed
-
- Zanetti M. Cathelicidins, multifunctional peptides of the innate immunity. J Leukoc Biol. 2004;75:39–38. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources