MDA5-positive dermatomyositis: an uncommon entity in Europe with variable clinical presentations
- PMID: 26557046
- PMCID: PMC4637993
- DOI: 10.1186/s12948-015-0031-y
MDA5-positive dermatomyositis: an uncommon entity in Europe with variable clinical presentations
Abstract
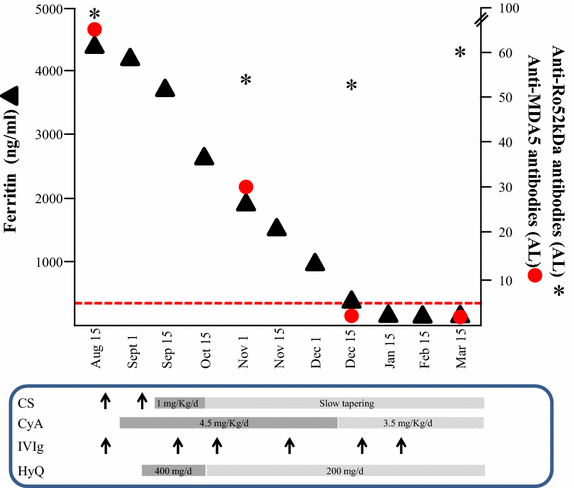
Clinically amyopathic dermatomyositis (CADM), described almost 50 years ago, is defined on the basis of still not validated criteria and characterized by skin findings almost without muscle weakness. Autoantibodies directed against the cytosolic pathogen sensor MDA5 (CADM 140) can mark this subtype of dermatomyositis which has been reported to associate, in particular ethnic groups, with severe progressive interstitial lung disease, poor prognosis and an hyperferritinemic status resembling hemophagocytic-like syndromes. MDA5 may be relevant in that Interferon-signature claimed to characterize inflammatory myopathies and dermatomyosits itself, but its role is not clear. However, the titre of anti-MDA5 autoantibodies seems to correlate with the outcome. In Caucasian populations the association between anti-MDA5 positive CADM and rapidly progressive interstitial lung disease seems to be weaker, but the limited numbers of patients described so far could explain the lack of statistical significance. As a fact, European patients with circulating anti-MDA5 autoantibodies may be clinically inhomogeneous and exhibit different rates of severity. The two patients affected by anti-MDA5 positive dermatomyositis described hereafter provide a clear example of the extreme variability of the disease in terms of laboratory findings and clinical features.
Keywords: CADM; Clinically amyopathic dermatomyositis; Dermatomyositis; MDA5.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Differential clinical features of patients with clinically amyopathic dermatomyositis who have circulating anti-MDA5 autoantibodies with or without myositis-associated autoantibodies.Respir Med. 2018 Jul;140:1-5. doi: 10.1016/j.rmed.2018.05.010. Epub 2018 May 22. Respir Med. 2018. PMID: 29957268
-
Serum cytokine profiles of patients with interstitial lung disease associated with anti-CADM-140/MDA5 antibody positive amyopathic dermatomyositis.Respir Med. 2015 Sep;109(9):1174-80. doi: 10.1016/j.rmed.2015.07.004. Epub 2015 Jul 9. Respir Med. 2015. PMID: 26187000
-
Clinical Significance of Serum Chitotriosidase Level in Anti-MDA5 Antibody-positive Dermatomyositis-associated Interstitial Lung Disease.J Rheumatol. 2019 Aug;46(8):935-942. doi: 10.3899/jrheum.180825. Epub 2019 May 15. J Rheumatol. 2019. PMID: 31092718
-
MDA5 autoantibody-another indicator of clinical diversity in dermatomyositis.Ann Transl Med. 2017 Apr;5(7):160. doi: 10.21037/atm.2017.03.94. Ann Transl Med. 2017. PMID: 28480196 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recurrence in long-term survivor of anti-MDA5 antibody-positive clinically amyopathic dermatomyositis: case series and literature review.Mod Rheumatol Case Rep. 2021 Jul;5(2):310-316. doi: 10.1080/24725625.2021.1886666. Epub 2021 Feb 25. Mod Rheumatol Case Rep. 2021. PMID: 33560195 Review.
Cited by
-
Multivariate logistic regression analysis of poor prognosis of dermatomyositis and clinical value of ferritin/Kl-6 in predicting prognosis.Skin Res Technol. 2024 May;30(5):e13701. doi: 10.1111/srt.13701. Skin Res Technol. 2024. PMID: 38682785 Free PMC article.
-
Systematic review and meta-analysis of prognostic factors for idiopathic inflammatory myopathy-associated interstitial lung disease.BMJ Open. 2018 Dec 16;8(12):e023998. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2018-023998. BMJ Open. 2018. PMID: 30559160 Free PMC article.
-
Bench to bedside review of myositis autoantibodies.Clin Mol Allergy. 2018 Mar 7;16:5. doi: 10.1186/s12948-018-0084-9. eCollection 2018. Clin Mol Allergy. 2018. PMID: 29540998 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Antimelanoma differentiation-associated gene 5 (anti-MDA5) antibody-positive dermatomyositis: clinical features and outcomes in a racially diverse patient cohort.BMC Rheumatol. 2025 Jan 9;9(1):5. doi: 10.1186/s41927-025-00455-5. BMC Rheumatol. 2025. PMID: 39789667 Free PMC article.
-
Rapidly progressive melanoma differentiation-associated protein 5-positive amyopathic dermatomyositis in an HIV-positive patient.JAAD Case Rep. 2017 Mar 22;3(2):158-161. doi: 10.1016/j.jdcr.2017.01.013. eCollection 2017 Mar. JAAD Case Rep. 2017. PMID: 28374003 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Andrejeva J, Childs KS, Young DF, Carlos TS, Stock N, Goodbourn S, Randall RE. The V proteins of paramyxoviruses bind the IFN-inducible RNA helicase, mda-5, and inhibit its activation of the IFN-beta promoter. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2004;101:17264–17269. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0407639101. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Kato H, Takeuchi O, Sato S, Yoneyama M, Yamamoto M, Matsui K, Uematsu S, Jung A, Kawai T, Ishii KJ, Yamaguchi O, Otsu K, Tsujimura T, Koh C-S, Reis e Sousa C, Matsuura Y, Fujita T, Akira S. Differential roles of MDA5 and RIG-I helicases in the recognition of RNA viruses. Nature. 2006;441:101–105. doi: 10.1038/nature04734. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

