Optimizing Rheumatoid Arthritis Therapy: Using Objective Measures of Disease Activity to Guide Treatment
- PMID: 26557229
- PMCID: PMC4636274
Optimizing Rheumatoid Arthritis Therapy: Using Objective Measures of Disease Activity to Guide Treatment
Abstract
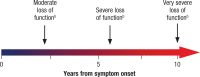
Background: Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) affects approximately 1.5 million individuals in the United States, or approximately 1% of the US adult population. In women, RA most often begins between age 30 and 60 years; in men, it often starts later in life. Patients with RA may have rapid declines in physical function that can begin early in the disease course. Disability increases most rapidly during the early years of the disease course, and if patients are not accurately diagnosed and do not receive appropriate care early, substantial functional declines may result.
Objective: To review strategies and clinical assessment tools that may optimize patient outcomes by using objective measures of disease activity.
Discussion: The goal of treatment for patients newly diagnosed with RA should be preventing joint damage from developing by employing early and aggressive approaches to therapy that minimize disease activity. Likewise, for established disease, treatment should be aimed at limiting the progression of existing joint damage. Substantial advances have been made in the treatment of RA over the past 2 decades, in large part as a result of better understanding of the biology of RA and the resultant introduction of biologic therapies. In 2010, an international task force published recommendations for a treat-to-target management approach to RA, much of which was based on the use of biologic drugs. This treatment strategy emphasized that the primary target in the treatment of patients with RA should be clinical remission or low disease activity. The tools necessary to measure RA disease activity are often incomplete, imprecise, or rely on a combination of physician and patient subjective evaluations. There is no one symptom, laboratory measure, or clinical tool that provides a truly accurate assessment of disease activity in patients with RA.
Conclusion: Thus, there is a large gap between what is recommended in clinical guidelines and the actual practice of rheumatologists. Better methods of assessing RA disease activity are still needed to enable widespread adoption of guidelines in the clinical community.
Keywords: clinical assessment; disease activity; disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs; multibiomarker test; objective measures; rheumatoid arthritis; treat-to-target approach.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Diagnosis and Management of Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Review.JAMA. 2018 Oct 2;320(13):1360-1372. doi: 10.1001/jama.2018.13103. JAMA. 2018. PMID: 30285183 Review.
-
New Rheumatoid Arthritis Treatments for 'Old' Patients: Results of a Systematic Review.Adv Ther. 2020 Sep;37(9):3676-3691. doi: 10.1007/s12325-020-01435-6. Epub 2020 Jul 23. Adv Ther. 2020. PMID: 32705531 Free PMC article.
-
Incorporating the treat-to-target concept in rheumatoid arthritis.J Manag Care Pharm. 2012 Nov-Dec;18(9):1-18. doi: 10.18553/jmcp.2012.18.S9-A.1. J Manag Care Pharm. 2012. PMID: 23206239 Free PMC article.
-
Early rheumatoid arthritis -- is there a window of opportunity?J Rheumatol Suppl. 2007 Nov;80:1-7. J Rheumatol Suppl. 2007. PMID: 17985417 Review.
-
The prevalence and types of discordance between physician perception and objective data from standardized measures of rheumatoid arthritis disease activity in real-world clinical practice in the US.BMC Rheumatol. 2019 Jul 4;3:25. doi: 10.1186/s41927-019-0073-8. eCollection 2019. BMC Rheumatol. 2019. PMID: 31312786 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Comparative analysis of US real-world dosing patterns and direct infusion-related costs for matched cohorts of rheumatoid arthritis patients treated with infliximab or intravenous golimumab.Clinicoecon Outcomes Res. 2019 Jan 15;11:99-110. doi: 10.2147/CEOR.S185547. eCollection 2019. Clinicoecon Outcomes Res. 2019. PMID: 30679916 Free PMC article.
-
99Tc-MDP treatment for the therapy of rheumatoid arthritis, choroidal neovascularisation and Graves' ophthalmopathy.Biomed Rep. 2016 Apr;4(4):400-402. doi: 10.3892/br.2016.609. Epub 2016 Feb 23. Biomed Rep. 2016. PMID: 27073620 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical and ultrasound optimization in rheumatoid arthritis for patients in sustained remission, can it work as a new optimization tool?J Ultrasound. 2025 Mar;28(1):81-87. doi: 10.1007/s40477-024-00963-z. Epub 2024 Oct 18. J Ultrasound. 2025. PMID: 39424691 Clinical Trial.
-
Comparing the effect of eye movement desensitization and reprocessing (EMDR) with guided imagery on pain severity in patients with rheumatoid arthritis.J Pain Res. 2018 Sep 28;11:2107-2113. doi: 10.2147/JPR.S158981. eCollection 2018. J Pain Res. 2018. PMID: 30319285 Free PMC article.
-
Optical Biosensors for the Detection of Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA) Biomarkers: A Comprehensive Review.Sensors (Basel). 2020 Nov 4;20(21):6289. doi: 10.3390/s20216289. Sensors (Basel). 2020. PMID: 33158306 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Landré-Beauvais AJ. The first description of rheumatoid arthritis. Unabridged text of the doctoral dissertation presented in 1800. Joint Bone Spine. 2001;68:130–143. - PubMed
-
- Garrod AB. The Nature and Treatment of Gout and Rheumatic Gout. London, England: Walton and Maberly; 1859.
-
- Arthritis Foundation. What is rheumatoid arthritis? www.arthritis.org/about-arthritis/types/rheumatoid-arthritis/what-is-rhe.... Accessed June 30, 2015.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous