Apogeotropic Posterior Semicircular Canal Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo: Some Clinical and Therapeutic Considerations
- PMID: 26557364
- PMCID: PMC4627115
- DOI: 10.4081/audiores.2015.130
Apogeotropic Posterior Semicircular Canal Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo: Some Clinical and Therapeutic Considerations
Abstract
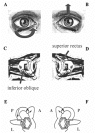
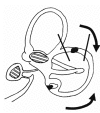
We lately reported the cases of patients complaining positional vertigo whose nystagmic pattern was that of a peripheral torsional vertical positional down beating nystagmus originating from a lithiasis of the non-ampullary arm of the posterior semicircular canal (PSC). We considered this particular pathological picture the apogeotropic variant of PSC benign paroxysmal positional vertigo (BPPV). Since the description of the pilot cases we observed more than 150 patients showing the same clinical sign and course of symptoms. In this paper we describe, in detail, both nystagmus of apogeotropic PSC BPPV (A-PSC BPPV) and symptoms reported by patients trying to give a reasonable explanation for these clinical features. Moreover we developed two specific physical therapies directed to cure A-PSC BPPV. Preliminary results of these techniques are related.
Keywords: 45° forced prolonged position; apogeotropic variant; demi Semont; down beating nystagmus; positional vertigo.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest: the authors declare no potential conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Brandt T, Steddin S. Current view of the mechanism of benign paroxysmal positional vertigo: cupulolithiasis or canalithiasis? J Vestib Res 1993;3:373-82. - PubMed
-
- Epley JM. New dimensions of benign paroxysmal positional vertigo. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 1980;88:599-605. - PubMed
-
- Hall SF, Ruby RRF, McClure JA. The mechanics of benign paroxysmal vertigo. J Otolaryngol 1979;8:151-8. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
