Central line complications
- PMID: 26557487
- PMCID: PMC4613416
- DOI: 10.4103/2229-5151.164940
Central line complications
Abstract
Central venous access is a common procedure performed in many clinical settings for a variety of indications. Central lines are not without risk, and there are a multitude of complications that are associated with their placement. Complications can present in an immediate or delayed fashion and vary based on type of central venous access. Significant morbidity and mortality can result from complications related to central venous access. These complications can cause a significant healthcare burden in cost, hospital days, and patient quality of life. Advances in imaging, access technique, and medical devices have reduced and altered the types of complications encountered in clinical practice; but most complications still center around vascular injury, infection, and misplacement. Recognition and management of central line complications is important when caring for patients with vascular access, but prevention is the ultimate goal. This article discusses common and rare complications associated with central venous access, as well as techniques to recognize, manage, and prevent complications.
Keywords: Bleeding; central line; complications; infection; pneumothorax.
Figures

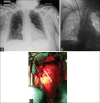



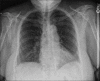
References
-
- McGee DC, Gould MK. Preventing complications of central venous catheterization. N Engl J Med. 2003;348:1123–33. - PubMed
-
- O’Grady NP, Alexander M, Burns LA, Dellinger EP, Garland J, Heard SO, et al. Healthcare Infection Control Practices Advisory Committee (HICPAC) (Appendix 1). Summary of recommendations: Guidelines for the prevention of intravascular catheter-related infections. Clin Infect Dis. 2011;52:1087–99. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Kusminsky RE. Complications of central venous catheterization. J Am Coll Surg. 2007;204:681–96. - PubMed
-
- Sznajder JI, Zveibil FR, Bitterman H, Weiner P, Bursztein S. Central vein catheterization. Failure and complication rates by three percutaneous approaches. Arch Intern Med. 1986;146:259–61. - PubMed
-
- Bhutta ST, Culp WC. Evaluation and management of central venous access complications. Tech Vasc Interv Radiol. 2011;14:217–24. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

