The Impact of Neutrons in Clinical Proton Therapy
- PMID: 26557501
- PMCID: PMC4617104
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2015.00235
The Impact of Neutrons in Clinical Proton Therapy
Abstract
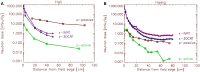
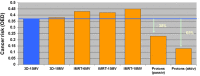
In proton therapy, high-energy proton beams cause the production of secondary neutrons. This leads to an unwanted dose contribution, which can be considerable for tissues outside of the target volume regarding the long-term health of cancer patients. Due to the high biological effectiveness of neutrons with regard to cancer induction, small neutron doses can be important. Published comparisons of neutron dose measurements and the corresponding estimates of cancer risk between different treatment modalities differ over orders of magnitude. In this report, the controversy about the impact of the neutron dose in proton therapy is critically discussed and viewed in the light of new epidemiological studies. In summary, the impact of neutron dose on cancer risk can be determined correctly only if the dose distributions are carefully measured or computed. It is important to include not only the neutron component into comparisons but also the complete deposition of energy as precisely as possible. Cancer risk comparisons between different radiation qualities, treatment machines, and techniques have to be performed under similar conditions. It seems that in the past, the uncertainty in the models which lead from dose to risk were overestimated when compared with erroneous dose comparisons. Current risk models used with carefully obtained dose distributions predict a second cancer risk reduction for active protons vs. photons and a more or less constant risk of passive protons vs. photons. Those findings are in general agreement with newly obtained epidemiologically results.
Keywords: neutrons; proton therapy; second cancer.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Measurements of the neutron dose equivalent for various radiation qualities, treatment machines and delivery techniques in radiation therapy.Phys Med Biol. 2014 May 21;59(10):2457-68. doi: 10.1088/0031-9155/59/10/2457. Epub 2014 Apr 28. Phys Med Biol. 2014. PMID: 24778349
-
Photonuclear dose calculations for high-energy photon beams from Siemens and Varian linacs.Med Phys. 2003 Aug;30(8):1990-2000. doi: 10.1118/1.1590436. Med Phys. 2003. PMID: 12945965
-
Characterization of the secondary neutron field produced during treatment of an anthropomorphic phantom with x-rays, protons and carbon ions.Phys Med Biol. 2014 Apr 21;59(8):2111-25. doi: 10.1088/0031-9155/59/8/2111. Epub 2014 Apr 2. Phys Med Biol. 2014. PMID: 24694920
-
Secondary neutrons in clinical proton radiotherapy: a charged issue.Radiother Oncol. 2008 Feb;86(2):165-70. doi: 10.1016/j.radonc.2007.12.003. Epub 2008 Jan 14. Radiother Oncol. 2008. PMID: 18192046 Review.
-
Dosimetry of clinical neutron and proton beams: an overview of recommendations.Radiat Prot Dosimetry. 2004;110(1-4):565-72. doi: 10.1093/rpd/nch221. Radiat Prot Dosimetry. 2004. PMID: 15353710 Review.
Cited by
-
Treatment plan comparison of proton vs photon radiotherapy for lower-grade gliomas.Phys Imaging Radiat Oncol. 2021 Nov 28;20:98-104. doi: 10.1016/j.phro.2021.11.008. eCollection 2021 Oct. Phys Imaging Radiat Oncol. 2021. PMID: 34888422 Free PMC article.
-
Consolidative mediastinal irradiation of malignant lymphoma using active scanning proton beams: clinical outcome and dosimetric comparison.Strahlenther Onkol. 2019 Jul;195(7):677-687. doi: 10.1007/s00066-019-01460-7. Epub 2019 Apr 10. Strahlenther Onkol. 2019. PMID: 30972453 English.
-
Measurements of fetal dose with Mevion S250i proton therapy system with HYPERSCAN.J Appl Clin Med Phys. 2023 May;24(5):e13957. doi: 10.1002/acm2.13957. Epub 2023 Apr 12. J Appl Clin Med Phys. 2023. PMID: 37043346 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of the Mini-ridge Filter's Impact on the Generation of Secondary Radiation in Synchrotron-based Proton Beam Therapy.J Med Phys. 2025 Jan-Mar;50(1):14-19. doi: 10.4103/jmp.jmp_206_24. Epub 2025 Mar 24. J Med Phys. 2025. PMID: 40256175 Free PMC article.
-
Proton versus Photon Radiotherapy for Pediatric Central Nervous System Malignancies: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Dosimetric Comparison Studies.J Oncol. 2019 Nov 27;2019:5879723. doi: 10.1155/2019/5879723. eCollection 2019. J Oncol. 2019. PMID: 31885580 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Siebers JV. Application of Monte Carlo to proton beam radiation therapy. In: Kling A, editor. Monte Carlo 2000 – Advanced Monte Carlo for Radiation Physics, Particle Transport Simulation and Applications. (Lisbon, Portugal: ) (2000) p. 1051–6.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

