All-Trans Retinoic Acid Induces Proliferation, Survival, and Migration in A549 Lung Cancer Cells by Activating the ERK Signaling Pathway through a Transcription-Independent Mechanism
- PMID: 26557664
- PMCID: PMC4628773
- DOI: 10.1155/2015/404368
All-Trans Retinoic Acid Induces Proliferation, Survival, and Migration in A549 Lung Cancer Cells by Activating the ERK Signaling Pathway through a Transcription-Independent Mechanism
Abstract
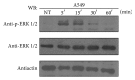
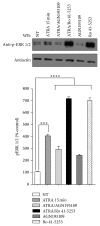
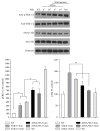
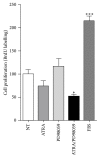
All-trans retinoic acid (ATRA) has been used as an antineoplastic because of its ability to promote proliferation, inhibition, and differentiation, primarily in leukemia; however, in other types of cancer, such as lung cancer, treatment with ATRA is restricted because not all the patients experience the same results. The ERK signaling pathway is dysregulated in cancer cells, including lung cancer, and this dysregulation promotes proliferation and cell invasion. In this study, we demonstrate that treatment with ATRA can activate the ERK signaling pathway by a transcription-independent mechanism through a signaling cascade that involves RARα and PI3K, promoting growth, survival, and migration in lung cancer cells. Until now, this mechanism was unknown in lung cancer cells. The inhibition of the ERK signaling pathway restores the beneficial effects of ATRA, reduces proliferation, increases apoptosis, and blocks the cell migration process in lung cancer cells. In conclusion, our results suggest that the combination of ATRA with ERK inhibitor in clinical trials for lung cancer is warranted.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Activation of Akt pathway by transcription-independent mechanisms of retinoic acid promotes survival and invasion in lung cancer cells.Mol Cancer. 2013 May 21;12:44. doi: 10.1186/1476-4598-12-44. Mol Cancer. 2013. PMID: 23693014 Free PMC article.
-
All-trans retinoic acid inhibits tumor growth of human osteosarcoma by activating Smad signaling-induced osteogenic differentiation.Int J Oncol. 2012 Jul;41(1):153-60. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2012.1426. Epub 2012 Apr 3. Int J Oncol. 2012. PMID: 22485251
-
Inhibition of all-trans-retinoic acid-induced proteasome activation potentiates the differentiating effect of retinoid in acute myeloid leukemia cells.Mol Carcinog. 2011 Jan;50(1):24-35. doi: 10.1002/mc.20687. Mol Carcinog. 2011. PMID: 20945414
-
Synergistic and additive effects of ATRA in combination with different anti-tumor compounds.Chem Biol Interact. 2018 Apr 1;285:69-75. doi: 10.1016/j.cbi.2018.02.021. Epub 2018 Feb 16. Chem Biol Interact. 2018. PMID: 29458017 Review.
-
Modulation of all-trans retinoic acid-induced MiRNA expression in neoplastic cell lines: a systematic review.BMC Cancer. 2019 Aug 30;19(1):866. doi: 10.1186/s12885-019-6081-7. BMC Cancer. 2019. PMID: 31470825 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Potential antitumour effect of all-trans retinoic acid on regorafenib-treated human colon cancer cell lines.Contemp Oncol (Pozn). 2023;27(3):198-210. doi: 10.5114/wo.2023.133742. Epub 2023 Dec 21. Contemp Oncol (Pozn). 2023. PMID: 38239861 Free PMC article.
-
The potential of retinoids for combination therapy of lung cancer: Updates and future directions.Pharmacol Res. 2019 Sep;147:104331. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2019.104331. Epub 2019 Jun 26. Pharmacol Res. 2019. PMID: 31254665 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Retinoic acid receptor alpha inhibits ferroptosis by promoting thioredoxin and protein phosphatase 1F in lung adenocarcinoma.Commun Biol. 2024 Jun 20;7(1):751. doi: 10.1038/s42003-024-06452-7. Commun Biol. 2024. PMID: 38902322 Free PMC article.
-
Preparation and in vitro characterization of retinoic acid-loaded poly(ε-caprolactone)-poly(ethylene glycol)-poly(ε-caprolactone) micelles.Res Pharm Sci. 2017 Dec;12(6):465-478. doi: 10.4103/1735-5362.217427. Res Pharm Sci. 2017. PMID: 29204175 Free PMC article.
-
Cellular retinol binding protein 1 transfection reduces proliferation and AKT-related gene expression in H460 non-small lung cancer cells.Mol Biol Rep. 2020 Sep;47(9):6879-6886. doi: 10.1007/s11033-020-05744-5. Epub 2020 Sep 9. Mol Biol Rep. 2020. PMID: 32909215 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

