Curcumin Enhanced Busulfan-Induced Apoptosis through Downregulating the Expression of Survivin in Leukemia Stem-Like KG1a Cells
- PMID: 26557682
- PMCID: PMC4628751
- DOI: 10.1155/2015/630397
Curcumin Enhanced Busulfan-Induced Apoptosis through Downregulating the Expression of Survivin in Leukemia Stem-Like KG1a Cells
Abstract
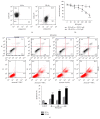
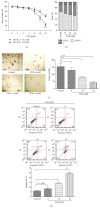
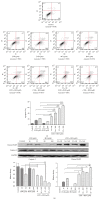
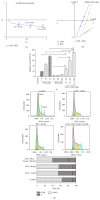
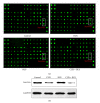
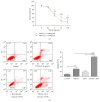
Leukemia relapse and nonrecurrence mortality (NRM) due to leukemia stem cells (LSCs) represent major problems following hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT). To eliminate LSCs, the sensitivity of LSCs to chemotherapeutic agents used in conditioning regimens should be enhanced. Curcumin (CUR) has received considerable attention as a result of its anticancer activity in leukemia and solid tumors. In this study, we investigated the cytotoxic effects and underlying mechanisms in leukemia stem-like KG1a cells exposed to busulfan (BUS) and CUR, either alone or in combination. KG1a cells exhibiting BUS-resistance demonstrated by MTT and annexin V/propidium iodide (PI) assays, compared with HL-60 cells. CUR induced cell growth inhibition and apoptosis in KG1a cells. Apoptosis of KG1a cells was significantly enhanced by treatment with CUR+BUS, compared with either agent alone. CUR synergistically enhanced the cytotoxic effect of BUS. Seven apoptosis-related proteins were modulated in CUR- and CUR+BUS-treated cells analyzed by proteins array analysis. Importantly, the antiapoptosis protein survivin was significantly downregulated, especially in combination group. Suppression of survivin with specific inhibitor YM155 significantly increased the susceptibility of KG1a cells to BUS. These results demonstrated that CUR could increase the sensitivity of leukemia stem-like KG1a cells to BUS by downregulating the expression of survivin.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Curcumin reduces the expression of survivin, leading to enhancement of arsenic trioxide-induced apoptosis in myelodysplastic syndrome and leukemia stem-like cells.Oncol Rep. 2016 Sep;36(3):1233-42. doi: 10.3892/or.2016.4944. Epub 2016 Jul 15. Oncol Rep. 2016. PMID: 27430728 Free PMC article.
-
Curcumin reduces expression of Bcl-2, leading to apoptosis in daunorubicin-insensitive CD34+ acute myeloid leukemia cell lines and primary sorted CD34+ acute myeloid leukemia cells.J Transl Med. 2011 May 19;9:71. doi: 10.1186/1479-5876-9-71. J Transl Med. 2011. PMID: 21595920 Free PMC article.
-
siRNA-mediated inhibition of survivin gene enhances the anti-cancer effect of etoposide in U-937 acute myeloid leukemia cells.Cell Mol Biol (Noisy-le-grand). 2016 May 30;62(6):44-9. Cell Mol Biol (Noisy-le-grand). 2016. PMID: 27262801
-
Curcumin-mediated regulation of Notch1/hairy and enhancer of split-1/survivin: molecular targeting in cholangiocarcinoma.J Surg Res. 2015 Oct;198(2):434-40. doi: 10.1016/j.jss.2015.03.029. Epub 2015 Mar 19. J Surg Res. 2015. PMID: 25890434 Review.
-
Effects of resveratrol, curcumin, berberine and other nutraceuticals on aging, cancer development, cancer stem cells and microRNAs.Aging (Albany NY). 2017 Jun 12;9(6):1477-1536. doi: 10.18632/aging.101250. Aging (Albany NY). 2017. PMID: 28611316 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Curcumin, a Multifaceted Hormetic Agent, Mediates an Intricate Crosstalk between Mitochondrial Turnover, Autophagy, and Apoptosis.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2020 Jul 18;2020:3656419. doi: 10.1155/2020/3656419. eCollection 2020. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2020. PMID: 32765806 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Alantolactone selectively ablates acute myeloid leukemia stem and progenitor cells.J Hematol Oncol. 2016 Sep 22;9(1):93. doi: 10.1186/s13045-016-0327-5. J Hematol Oncol. 2016. PMID: 27658462 Free PMC article.
-
Synthesis and biological evaluation of dithiocarbamate esters of parthenolide as potential anti-acute myelogenous leukaemia agents.J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem. 2018 Dec;33(1):1376-1391. doi: 10.1080/14756366.2018.1490734. J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem. 2018. PMID: 30208745 Free PMC article.
-
Integrative Hematology: State of the Art.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jan 15;24(2):1732. doi: 10.3390/ijms24021732. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36675247 Free PMC article. Review.
-
E35 ablates acute leukemia stem and progenitor cells in vitro and in vivo.J Cell Physiol. 2020 Nov;235(11):8023-8034. doi: 10.1002/jcp.29457. Epub 2020 Jan 21. J Cell Physiol. 2020. PMID: 31960417 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Thomas E. D. A review of the results of human marrow transplantation in Seattle. Nihon Ketsueki Gakkai Zasshi. 1977;40:863–872. - PubMed
-
- Pavletic S. Z., Kumar S., Mohty M., et al. NCI first international workshop on the biology, prevention, and treatment of relapse after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation: report from the committee on the epidemiology and natural history of relapse following allogeneic cell transplantation. Biology of Blood and Marrow Transplantation. 2010;16(7):871–890. doi: 10.1016/j.bbmt.2010.04.004. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

