Over-the-Counter Hearing Aids: A Lost Decade for Change
- PMID: 26557701
- PMCID: PMC4628714
- DOI: 10.1155/2015/827463
Over-the-Counter Hearing Aids: A Lost Decade for Change
Abstract
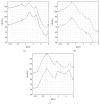
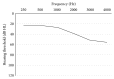
Background: Hearing aids sold directly to consumers in retail stores or through the internet, without individual prescription by audiological professionals, are termed over-the-counter (OTC) devices. This study aimed to determine whether there was any change in the electroacoustic characteristics of OTC devices compared to research carried out a decade earlier. The previous results indicated that most OTC devices were low-frequency-emphasis devices and were unsuitable for elderly people with presbycusis, who were likely to be the major consumers of these products.
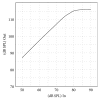
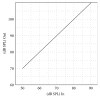
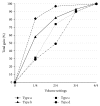
Methods: Ten OTC devices were selected and their electroacoustic performance was measured. Appropriate clients for the OTC devices were derived, using four linear prescription formulae, and OTC suitability for elderly persons with presbycusis was investigated.
Results: OTC electroacoustic characteristics were similar to those in the earlier study. Most OTC devices were not acoustically appropriate for potential consumers with presbycusis. Although several of the devices could match prescriptive targets for individuals with presbycusis, their poor electroacoustic performance--including ineffective volume control function, high equivalent input noise, and irregular frequency response--may override their potential benefit.
Conclusion: The low-cost OTC devices were generally not suitable for the main consumers of these products, and there has been little improvement in the appropriateness of these devices over the past decade.
Figures


References
-
- Boswell S. FDA rejects citizen petitions for over-the-counter hearing aids. ASHA Leader. 2004;9(8, article 1)
-
- United States Food and Drug Administration: How to get hearing aids, http://www.fda.gov/MedicalDevices/ProductsandMedicalProcedures/HomeHealt....
-
- Cheng C. M. Over-the-counter hearing aids: electroacoustic characteristics and possible target client groups [M.S. thesis] Hong Kong: Department of Speech and Hearing Sciences, University of Hong Kong; 1998. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

