Trigonella foenum (Fenugreek) Induced Apoptosis in Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cell Line, HepG2, Mediated by Upregulation of p53 and Proliferating Cell Nuclear Antigen
- PMID: 26557712
- PMCID: PMC4628703
- DOI: 10.1155/2015/914645
Trigonella foenum (Fenugreek) Induced Apoptosis in Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cell Line, HepG2, Mediated by Upregulation of p53 and Proliferating Cell Nuclear Antigen
Abstract
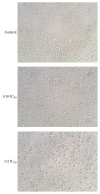
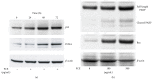
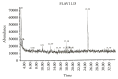
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is one of the most common cancers worldwide and most current therapies are of limited efficacy. Trigonella foenum (Fenugreek) is a traditional herbal plant with antitumor activity, although the mechanisms of its activity remain unclear. Herein, a crude methanol extract was prepared from Fenugreek seeds (FCE) and its anticancer mechanism was evaluated, using HepG2 cell line. Growth-inhibitory effect and apoptosis induction of HepG2 cells were evidenced by MTT assay, cell morphology alteration, apoptosis enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay, flow cytometric analysis, caspase-3 activity, and expression of p53, proapoptotic protein, Bax, and proliferating cell nuclear antigen (PCNA) after (100 ∼ 500 μg/mL) FCE treatment for 48 h. Furthermore, FCE was analyzed by Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry (GC/MS). Our results revealed that FCE treatment for 48 h showed a cytotoxic effect and apoptosis induction in a dose-dependent manner that was mediated by upregulation of p53, Bax, PCNA, and caspase-3 activation in HepG2 cells. GC-MS analysis of FCE showed the presence of fourteen bioactive compounds such as Terpenoids and Flavonoids, including two main constituents with anticancer activity, Squalene and Naringenin (27.71% and 24.05%), respectively. Our data introduced FCE as a promising nontoxic herbal with therapeutic potential to induce apoptosis in HepG2 cells through p53, Bax, and PCNA upregulation in caspase-3 dependent manner.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Fenugreek induced apoptosis in breast cancer MCF-7 cells mediated independently by fas receptor change.Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2013;14(10):5783-8. doi: 10.7314/apjcp.2013.14.10.5783. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2013. PMID: 24289578
-
Novel Anti-Tubulin Compounds from Trigonella foenum-graecum Seeds; Insights into In-vitro and Molecular Docking Studies.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2021 Oct 5;15:4195-4211. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S320793. eCollection 2021. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2021. PMID: 34675483 Free PMC article.
-
Fenugreek, a naturally occurring edible spice, kills MCF-7 human breast cancer cells via an apoptotic pathway.Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2011;12(12):3299-304. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2011. PMID: 22471470
-
Cell Growth Inhibition, DNA Fragmentation and Apoptosis-Inducing Properties of Household-Processed Leaves and Seeds of Fenugreek (Trigonella Foenum-Graecum Linn.) against HepG2, HCT-116, and MCF-7 Cancerous Cell Lines.Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2023 Jan 19;45(2):936-953. doi: 10.3390/cimb45020060. Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2023. PMID: 36826005 Free PMC article.
-
Anticancer potential of Trigonella foenum graecum: Cellular and molecular targets.Biomed Pharmacother. 2017 Jun;90:479-491. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2017.03.071. Epub 2017 Apr 6. Biomed Pharmacother. 2017. PMID: 28391170 Review.
Cited by
-
Methanolic Fenugreek Seed Extract Induces p53-Dependent Mitotic Catastrophe in Breast Cancer Cells, Leading to Apoptosis.J Inflamm Res. 2021 Apr 16;14:1511-1535. doi: 10.2147/JIR.S300025. eCollection 2021. J Inflamm Res. 2021. PMID: 33889009 Free PMC article.
-
Cytotoxic activity of standardized extracts, a fraction, and individual secondary metabolites from fenugreek seeds against SKOV-3, HeLa and MOLT-4 cell lines.Pharm Biol. 2021 Dec;59(1):424-437. doi: 10.1080/13880209.2021.1903047. Pharm Biol. 2021. PMID: 33849376 Free PMC article.
-
Cytotoxic Effect of Bromelain on HepG2 Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cell Line.Appl Biochem Biotechnol. 2021 Jun;193(6):1873-1897. doi: 10.1007/s12010-021-03505-z. Epub 2021 Mar 18. Appl Biochem Biotechnol. 2021. PMID: 33735410
-
A steroidal derivative from Trigonella foenum graecum L. that induces apoptosis in vitro and in vivo.J Food Drug Anal. 2019 Jan;27(1):231-239. doi: 10.1016/j.jfda.2018.05.001. Epub 2018 May 26. J Food Drug Anal. 2019. PMID: 30648576 Free PMC article.
-
Synergistic antiproliferative effects of curcumin and celecoxib in hepatocellular carcinoma HepG2 cells.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2018 Dec;391(12):1399-1410. doi: 10.1007/s00210-018-1557-6. Epub 2018 Aug 28. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2018. PMID: 30155693
References
-
- Abdel-Hamid N. Update to risk factors of HCC. International Journal of Medicine and Medical Sciences. 2009;1(3):38–43.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

