Medical Therapy of Fibrostenotic Crohn's Disease
- PMID: 26557834
- PMCID: PMC4620591
- DOI: 10.1159/000435868
Medical Therapy of Fibrostenotic Crohn's Disease
Abstract
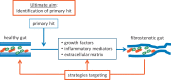
Introduction: The present review serves to provide a concise overview of the current knowledge on therapeutic strategies with regard to fibrostenotic lesions in Crohn's disease.
Methods: A literature search was performed focusing on the last 5 years, and current concepts of pathophysiology, epidemiology, and treatment have been summarized.
Results: Fibrostenotic lesions in Crohn's disease are currently considered to be a consequence of the chronic inflammatory nature of the disease. Hence, therapeutic strategies are limited to the concept that early treatment of the inflammatory lesions can prevent structural changes, and to various endoscopic and surgical approaches. Direct targeting of the fibrostenotic lesion itself has not been the focus until now. This review will provide an overview of the pathophysiology and epidemiology of fibrostenotic lesions including current therapeutic approaches. Since research with regard to other organ systems and fibrosis is far more advanced, current strategies from available studies in these areas will be discussed. The results and the potential impact for Crohn's disease will be considered.
Conclusion: The vision of these approaches is to reverse structural changes and restore normal function.
Keywords: Crohn's disease; Fibrosis; Stenosis.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Appropriate therapy for fistulizing and fibrostenotic Crohn's disease: Results of a multidisciplinary expert panel - EPACT II.J Crohns Colitis. 2009 Dec;3(4):250-6. doi: 10.1016/j.crohns.2009.06.001. Epub 2009 Aug 22. J Crohns Colitis. 2009. PMID: 21172283
-
Anoperineal lesions in Crohn's disease: French recommendations for clinical practice.Tech Coloproctol. 2017 Sep;21(9):683-691. doi: 10.1007/s10151-017-1684-y. Epub 2017 Sep 19. Tech Coloproctol. 2017. PMID: 28929282 Review.
-
Assessment of inflammatory and fibrotic stenoses in patients with Crohn's disease using contrast-enhanced ultrasound and computerized algorithm: a pilot study.Digestion. 2011;83(4):263-8. doi: 10.1159/000321389. Epub 2011 Jan 28. Digestion. 2011. PMID: 21273775
-
Clinical features and quality of life in patients with different phenotypes of Crohn's disease of the ileal pouch.Dis Colon Rectum. 2007 Sep;50(9):1450-9. doi: 10.1007/s10350-007-0284-8. Dis Colon Rectum. 2007. PMID: 17665259
-
Predictors of fibrostenotic Crohn's disease.Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2011 Sep;17(9):2000-7. doi: 10.1002/ibd.21627. Epub 2011 Feb 9. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2011. PMID: 21308880 Review.
Cited by
-
Shear Wave and Strain Elastography in Crohn's Disease-A Systematic Review.Diagnostics (Basel). 2021 Sep 3;11(9):1609. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics11091609. Diagnostics (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34573952 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated factor 5 enhances perianal fistulizing Crohn's disease through epithelial-mesenchymal transition.Cytojournal. 2024 Dec 31;21:82. doi: 10.25259/Cytojournal_148_2024. eCollection 2024. Cytojournal. 2024. PMID: 39917000 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Friedman SL, Sheppard D, Duffield JS, Violette S. Therapy for fibrotic diseases: nearing the starting line. Sci Transl Med. 2013;5:167sr161. - PubMed
-
- Fichtner-Feigl S, Young CA, Kitani A, Geissler EK, Schlitt HJ, Strober W. IL-13 signaling via IL-13R alpha2 induces major downstream fibrogenic factors mediating fibrosis in chronic TNBS colitis. Gastroenterology. 2008;135:2003–2013. 2013.e2001-2007. - PubMed
-
- Fichtner-Feigl S, Strober W, Kawakami K, Puri RK, Kitani A. IL-13 signaling through the IL-13alpha2 receptor is involved in induction of TGF-beta1 production and fibrosis. Nat Med. 2006;12:99–106. - PubMed
-
- Biancheri P, Di Sabatino A, Ammoscato F, Facciotti F, Caprioli F, Curciarello R, Hoque SS, Ghanbari A, Joe-Njoku I, Giuffrida P, Rovedatti L, Geginat J, Corazza GR, MacDonald TT. Absence of a role for interleukin-13 in inflammatory bowel disease. Eur J Immunol. 2014;44:370–385. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources