Notch signaling controls chondrocyte hypertrophy via indirect regulation of Sox9
- PMID: 26558140
- PMCID: PMC4640428
- DOI: 10.1038/boneres.2015.21
Notch signaling controls chondrocyte hypertrophy via indirect regulation of Sox9
Abstract
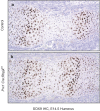
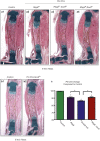
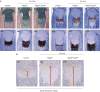
RBPjk-dependent Notch signaling regulates both the onset of chondrocyte hypertrophy and the progression to terminal chondrocyte maturation during endochondral ossification. It has been suggested that Notch signaling can regulate Sox9 transcription, although how this occurs at the molecular level in chondrocytes and whether this transcriptional regulation mediates Notch control of chondrocyte hypertrophy and cartilage development is unknown or controversial. Here we have provided conclusive genetic evidence linking RBPjk-dependent Notch signaling to the regulation of Sox9 expression and chondrocyte hypertrophy by examining tissue-specific Rbpjk mutant (Prx1Cre;Rbpjk(f/f) ), Rbpjk mutant/Sox9 haploinsufficient (Prx1Cre;Rbpjk(f/f);Sox9(f/+) ), and control embryos for alterations in SOX9 expression and chondrocyte hypertrophy during cartilage development. These studies demonstrate that Notch signaling regulates the onset of chondrocyte maturation in a SOX9-dependent manner, while Notch-mediated regulation of terminal chondrocyte maturation likely functions independently of SOX9. Furthermore, our in vitro molecular analyses of the Sox9 promoter and Notch-mediated regulation of Sox9 gene expression in chondrogenic cells identified the ability of Notch to induce Sox9 expression directly in the acute setting, but suppresses Sox9 transcription with prolonged Notch signaling that requires protein synthesis of secondary effectors.
Figures



References
-
- Kronenberg HM. Developmental regulation of the growth plate. Nature 2003; 423: 332–336. - PubMed
-
- Foster JW, Dominguez-Steglich MA, Guioli S et al. Campomelic dysplasia and autosomal sex reversal caused by mutations in an SRY-related gene. Nature 1994; 372: 525–530. - PubMed
-
- Wagner T, Wirth J, Meyer J et al. Autosomal sex reversal and campomelic dysplasia are caused by mutations in and around the SRY-related gene SOX9. Cell 1994; 79: 1111–1120. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

