Mesalazine preparations for the treatment of ulcerative colitis: Are all created equal?
- PMID: 26558148
- PMCID: PMC4635154
- DOI: 10.4292/wjgpt.v6.i4.137
Mesalazine preparations for the treatment of ulcerative colitis: Are all created equal?
Abstract
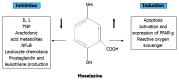
Oral mesalazine (also known as mesalamine) is a 5-aminosalicylic acid compound used in the treatment of mild to moderate ulcerative colitis, with high rates of efficacy in induction and maintenance of remission. The therapeutic effect of mesalazine occurs topically at the site of diseased colonic mucosa. A myriad of oral mesalazine preparations have been formulated with various drug delivery methods to minimize systemic absorption and maximise drug availability at the inflamed colonic epithelium. It remains unclear whether different oral mesalazine formulations are bioequivalent. This review aims to evaluate the differences between mesalazine formulations based on the currently available literature and explore factors which may influence the selection of one agent above another.
Keywords: Colitis; Drug delivery systems; Mesalamine; Sulfasalazine; Therapeutic equivalency; Ulcerative.
Figures

References
-
- Sutherland L, Roth D, Beck P, May G, Makiyama K. Oral 5-aminosalicylic acid for maintenance of remission in ulcerative colitis. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2002;(4):CD000544. - PubMed
-
- Ligumsky M, Karmeli F, Sharon P, Zor U, Cohen F, Rachmilewitz D. Enhanced thromboxane A2 and prostacyclin production by cultured rectal mucosa in ulcerative colitis and its inhibition by steroids and sulfasalazine. Gastroenterology. 1981;81:444–449. - PubMed
-
- Hawkey CJ, Boughton-Smith NK, Whittle BJ. Modulation of human colonic arachidonic acid metabolism by sulfasalazine. Dig Dis Sci. 1985;30:1161–1165. - PubMed
-
- Ahnfelt-Rønne I, Nielsen OH, Christensen A, Langholz E, Binder V, Riis P. Clinical evidence supporting the radical scavenger mechanism of 5-aminosalicylic acid. Gastroenterology. 1990;98:1162–1169. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

