Alteration of Zeta potential and membrane permeability in bacteria: a study with cationic agents
- PMID: 26558175
- PMCID: PMC4633473
- DOI: 10.1186/s40064-015-1476-7
Alteration of Zeta potential and membrane permeability in bacteria: a study with cationic agents
Abstract
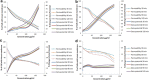
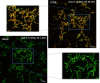
In the present study, we have tried to establish the correlation between changes in Zeta potential with that of cell surface permeability using bacteria (Escherichia coli and Staphylococcus aureus). An effort has been made to establish Zeta potential as a possible marker for the assessment of membrane damage, with a scope for predicting alteration of cell viability. Cationic agents like, cetyl trimethyl ammonium bromide and polymyxin B were used for inducing alteration of Zeta potential, and the changes occurring in the membrane permeability were studied. In addition, assessment of poly-dispersity index (PDI), cell viability along with confocal microscopic analysis were performed. Based on our results, it can be suggested that alteration of Zeta potential may be correlated to the enhancement of membrane permeability and PDI, and it was observed that beyond a critical point, it leads to cell death (both Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria). The present findings can not only be used for studying membrane active molecules but also for understanding the surface potential versus permeability relationship.
Keywords: Cell viability; Membrane permeability; Polydispersity index (PDI); Zeta potential.
Figures


References
-
- Alves CS, Melo MN, Franquelim HG, Ferre R, Planas M, Feliu L, Bardají E, Kowalczyk W, Andreu D, Santos NC, Fernandes MX, Castanho MA. Escherichia coli cell surface perturbation and disruption induced by antimicrobial peptides BP100 and pepR. J Biol Chem. 2010;285(36):27536–27544. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.130955. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

