When to initiate renal replacement therapy: The trend of dialysis initiation
- PMID: 26558189
- PMCID: PMC4635372
- DOI: 10.5527/wjn.v4.i5.521
When to initiate renal replacement therapy: The trend of dialysis initiation
Abstract
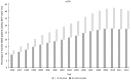
The timing of renal replacement therapy for patients with end-stage renal disease has been subject to considerable variation. The United States Renal Data System shows an ascending trend of early dialysis initiation until 2010, at which point it decreased slightly for the following 2 years. In the 1990s, nephrologists believed that early initiation of dialysis could improve patient survival. Based on the Canadian-United States Peritoneal Dialysis study, the National Kidney Foundation Dialysis Outcomes Quality Initiative recommended that dialysis should be initiated early. Since 2001, several observational studies and 1 randomized controlled trial have found no beneficial effect when patients were placed on dialysis early. In contrast, they found that an increase in mortality was associated with early dialysis initiation. The most recent dialysis initiation guidelines recommend that dialysis should be initiated at an estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) of greater than or equal to 6 mL/min per 1.73 m(2). Nevertheless, the decision to start dialysis is mainly based on a predefined eGFR value, and no convincing evidence has demonstrated that patients would benefit from early dialysis initiation as indicated by the eGFR. Even today, the optimal dialysis initiation time remains unknown. The decision of when to start dialysis should be based on careful clinical evaluation.
Keywords: Creatinine clearance; Dialysis; End-stage renal disease; Estimated glomerular filtration rate; Renal replacement therapy; Survival.
Figures
References
-
- US Renal Data System. USRDS 2014 Annual data report: Atlas of chronic kidney disease and end-stage renal disease in the United States. Available from: http://www.usrds.org/2014/view/Default.aspx. - PubMed
-
- Hakim RM, Lazarus JM. Initiation of dialysis. J Am Soc Nephrol. 1995;6:1319–1328. - PubMed
-
- Rosansky SJ, Cancarini G, Clark WF, Eggers P, Germaine M, Glassock R, Goldfarb DS, Harris D, Hwang SJ, Imperial EB, et al. Dialysis initiation: what’s the rush? Semin Dial. 2013;26:650–657. - PubMed
-
- Murtagh FE, Addington-Hall J, Higginson IJ. The prevalence of symptoms in end-stage renal disease: a systematic review. Adv Chronic Kidney Dis. 2007;14:82–99. - PubMed
-
- Cohen SD, Norris L, Acquaviva K, Peterson RA, Kimmel PL. Screening, diagnosis, and treatment of depression in patients with end-stage renal disease. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2007;2:1332–1342. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

