Management of hypotony and flat anterior chamber associated with glaucoma filtration surgery
- PMID: 26558207
- PMCID: PMC4630993
- DOI: 10.3980/j.issn.2222-3959.2015.05.17
Management of hypotony and flat anterior chamber associated with glaucoma filtration surgery
Abstract
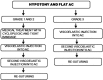
Aim: To determine the effectiveness of pharmacological and interventional treatment of hypotony and flat anterior chamber (FAC) resulting from glaucoma filtration surgery.
Methods: We retrospectively examined the medical records of fifty-two trabeculectomy patients (52 eyes) who developed postoperative hypotony and FAC. The management and associated complications of hypotony, changing intraocular pressure (IOP) and best corrected visual acuity (BCVA) were evaluated.
Result: Of the 52 patients with hypotony, 29 (56%) had a grade 1 FAC, 21 (40%) had a grade 2 FAC, and only 2 had a grade 3 FAC. There was no significant difference between the mean preoperative IOP and the mean IOP at three and six months after surgery. Thirteen eyes (25%) required antiglaucomatous medication three months after surgery. The mean BCVA at 6mo after surgery was significantly reduced as compared with the mean preoperative BCVA.
Conclusion: Hypotonia and FAC following trabeculectomy are associated with troublesome complications that require pharmacological and/or surgical treatment. Thus, close follow-up is essential for affected patients.
Keywords: flat anterior chamber; hypotony; trabeculectomy.
Similar articles
-
Risk factors for flat anterior chamber after glaucoma filtration surgery.Int J Ophthalmol. 2018 Aug 18;11(8):1322-1329. doi: 10.18240/ijo.2018.08.12. eCollection 2018. Int J Ophthalmol. 2018. PMID: 30140636 Free PMC article.
-
Hypotony Management through Transconjunctival Scleral Flap Resuturing: Analysis of Surgical Outcomes and Success Predictors.J Curr Glaucoma Pract. 2017 May-Aug;11(2):58-62. doi: 10.5005/jp-journals-10028-1224. Epub 2017 Aug 5. J Curr Glaucoma Pract. 2017. PMID: 28924340 Free PMC article.
-
Aductive laser iridoplasty and laser goniopuncture after non-perforating trabeculectomy.Cesk Slov Oftalmol. 2013 Mar;69(1):3-7. Cesk Slov Oftalmol. 2013. PMID: 23822595
-
Shallow Anterior Chamber After Trabeculectomy: Risk Reduction by Use of Removable Compression Sutures.J Glaucoma. 2016 Feb;25(2):223-7. doi: 10.1097/IJG.0000000000000151. J Glaucoma. 2016. PMID: 25264999
-
Does Chronic Hypotony following Trabeculectomy Represent Treatment Failure?J Curr Glaucoma Pract. 2015 Jan-Apr;9(1):12-5. doi: 10.5005/jp-journals-10008-1176. Epub 2015 Jan 15. J Curr Glaucoma Pract. 2015. PMID: 26997826 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Corneal Opacification and Spontaneous Recovery following Injection of Healon5 into the Corneal Stroma during Intervention for Postoperative Hypotony.Case Rep Ophthalmol. 2020 Jul 3;11(2):263-267. doi: 10.1159/000508604. eCollection 2020 May-Aug. Case Rep Ophthalmol. 2020. PMID: 32774290 Free PMC article.
-
Trend of glaucoma internal filtration surgeries in a tertiary hospital in China.Int J Ophthalmol. 2023 Feb 18;16(2):251-259. doi: 10.18240/ijo.2023.02.12. eCollection 2023. Int J Ophthalmol. 2023. PMID: 36816210 Free PMC article.
-
Bleb resuscitation of failing, leaking and dysfunctional blebs: A review.Indian J Ophthalmol. 2025 Mar 1;73(Suppl 2):S197-S206. doi: 10.4103/IJO.IJO_1233_24. Epub 2025 Feb 21. Indian J Ophthalmol. 2025. PMID: 39982080 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Outcome of Trabeculectomy with Collagen Matrix Implant versus Mitomycin C in Primary Glaucoma: A Comparative Study.Int J Appl Basic Med Res. 2021 Apr-Jun;11(2):80-84. doi: 10.4103/ijabmr.IJABMR_609_20. Epub 2021 Apr 8. Int J Appl Basic Med Res. 2021. PMID: 33912426 Free PMC article.
-
Short-term efficacy and safety of PreserFlo MicroShunt in Japanese patients with medically treated primary open-angle glaucoma.Jpn J Ophthalmol. 2025 Mar;69(2):287-295. doi: 10.1007/s10384-024-01159-y. Epub 2025 Jan 18. Jpn J Ophthalmol. 2025. PMID: 39826074
References
-
- Cairns JE. Trabeculectomy. Preliminary report of a new method. Am J Ophthalmol. 1968;66(4):673–679. - PubMed
-
- Hussain R, Clarke JC, Seah SK, Khaw PT. A review of trabeculectomy in East Asian people-the influence of race. Eye(Lond) 2005;19(3):243–252. - PubMed
-
- Edmunds B, Thompson JR, Salmon JF, Wormald RP. The National Survey of Trabeculectomy. III. Early and late complications. Eye(Lond) 2002;16(3):297–303. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources