Guanine nucleotide binding to the Bateman domain mediates the allosteric inhibition of eukaryotic IMP dehydrogenases
- PMID: 26558346
- PMCID: PMC4660370
- DOI: 10.1038/ncomms9923
Guanine nucleotide binding to the Bateman domain mediates the allosteric inhibition of eukaryotic IMP dehydrogenases
Abstract
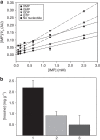
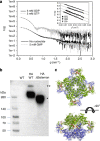
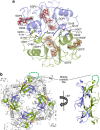
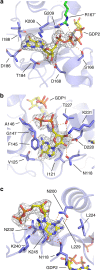
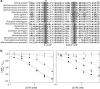
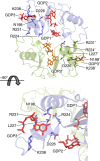
Inosine-5'-monophosphate dehydrogenase (IMPDH) plays key roles in purine nucleotide metabolism and cell proliferation. Although IMPDH is a widely studied therapeutic target, there is limited information about its physiological regulation. Using Ashbya gossypii as a model, we describe the molecular mechanism and the structural basis for the allosteric regulation of IMPDH by guanine nucleotides. We report that GTP and GDP bind to the regulatory Bateman domain, inducing octamers with compromised catalytic activity. Our data suggest that eukaryotic and prokaryotic IMPDHs might have developed different regulatory mechanisms, with GTP/GDP inhibiting only eukaryotic IMPDHs. Interestingly, mutations associated with human retinopathies map into the guanine nucleotide-binding sites including a previously undescribed non-canonical site and disrupt allosteric inhibition. Together, our results shed light on the mechanisms of the allosteric regulation of enzymes mediated by Bateman domains and provide a molecular basis for certain retinopathies, opening the door to new therapeutic approaches.
Figures
References
-
- Chong C. R. et al.. Identification of type 1 inosine monophosphate dehydrogenase as an antiangiogenic drug target. J. Med. Chem. 49, 2677–2680 (2006). - PubMed
-
- Jayaram H. N., Cooney D. A., Grusch M. & Krupitza G. Consequences of IMP dehydrogenase inhibition, and its relationship to cancer and apoptosis. Curr. Med. Chem. 6, 561–574 (1999). - PubMed
-
- Allison A. C. & Eugui E. M. Mycophenolate mofetil and its mechanisms of action. Immunopharmacology 47, 85–118 (2000). - PubMed
-
- Braun-Sand S. B. & Peetz M. Inosine monophosphate dehydrogenase as a target for antiviral, anticancer, antimicrobial and immunosuppressive therapeutics. Future Med. Chem. 2, 81–92 (2010). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

