The GH5 1,4-β-mannanase from Bifidobacterium animalis subsp. lactis Bl-04 possesses a low-affinity mannan-binding module and highlights the diversity of mannanolytic enzymes
- PMID: 26558435
- PMCID: PMC4642672
- DOI: 10.1186/s12858-015-0055-4
The GH5 1,4-β-mannanase from Bifidobacterium animalis subsp. lactis Bl-04 possesses a low-affinity mannan-binding module and highlights the diversity of mannanolytic enzymes
Abstract
Background: β-Mannans are abundant and diverse plant structural and storage polysaccharides. Certain human gut microbiota members including health-promoting Bifidobacterium spp. catabolize dietary mannans. Little insight is available on the enzymology of mannan deconstruction in the gut ecological niche. Here, we report the biochemical properties of the first family 5 subfamily 8 glycoside hydrolase (GH5_8) mannanase from the probiotic bacterium Bifidobacterium animalis subsp. lactis Bl-04 (BlMan5_8).
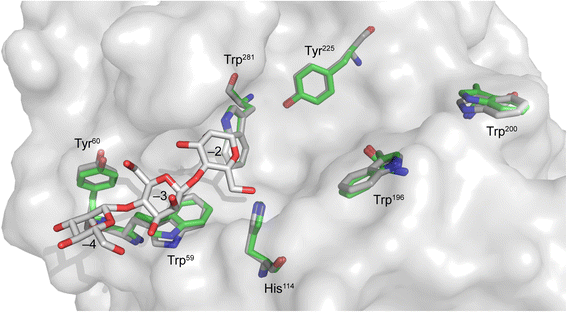
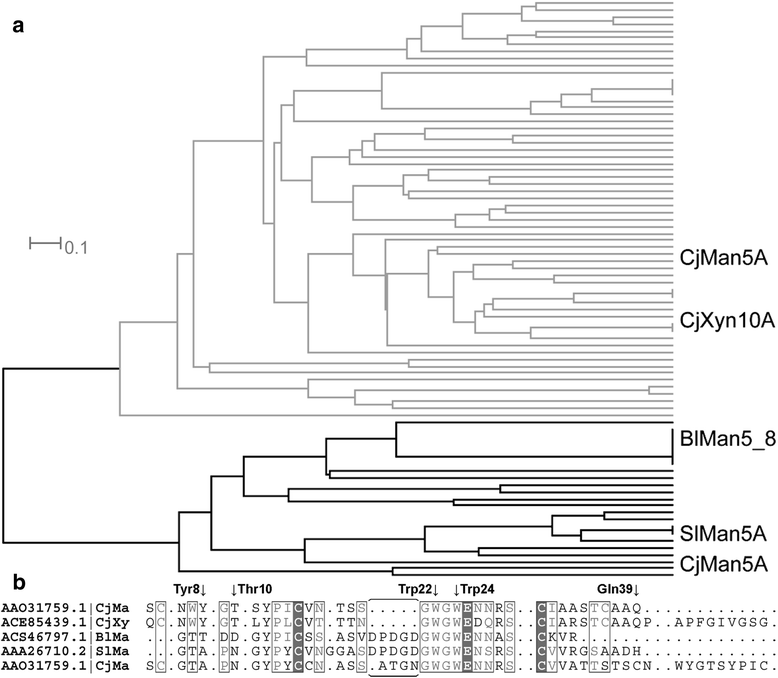
Results: BlMan5_8 possesses a novel low affinity carbohydrate binding module (CBM) specific for soluble mannan and displays the highest catalytic efficiency reported to date for a GH5 mannanase owing to a very high k cat (1828 ± 87 s(-1)) and a low K m (1.58 ± 0.23 g · L(-1)) using locust bean galactomannan as substrate. The novel CBM of BlMan5_8 mediates increased binding to soluble mannan based on affinity electrophoresis. Surface plasmon resonance analysis confirmed the binding of the CBM10 to manno-oligosaccharides, albeit with slightly lower affinity than the catalytic module of the enzyme. This is the first example of a low-affinity mannan-specific CBM, which forms a subfamily of CBM10 together with close homologs present only in mannanases. Members of this new subfamily lack an aromatic residue mediating binding to insoluble cellulose in canonical CBM10 members consistent with the observed low mannan affinity.
Conclusion: BlMan5_8 is evolved for efficient deconstruction of soluble mannans, which is reflected by an exceptionally low K m and the presence of an atypical low affinity CBM, which increases binding to specifically to soluble mannan while causing minimal decrease in catalytic efficiency as opposed to enzymes with canonical mannan binding modules. These features highlight fine tuning of catalytic and binding properties to support specialization towards a preferred substrate, which is likely to confer an advantage in the adaptation to competitive ecological niches.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The modular architecture of Cellvibrio japonicus mannanases in glycoside hydrolase families 5 and 26 points to differences in their role in mannan degradation.Biochem J. 2003 May 1;371(Pt 3):1027-43. doi: 10.1042/BJ20021860. Biochem J. 2003. PMID: 12523937 Free PMC article.
-
Unravelling biochemical and structural features of Bacillus licheniformis GH5 mannanase using site-directed mutagenesis and high-resolution protein crystallography studies.Int J Biol Macromol. 2024 Aug;274(Pt 2):133182. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2024.133182. Epub 2024 Jun 15. Int J Biol Macromol. 2024. PMID: 38885857
-
A cellulose-binding module of the Trichoderma reesei beta-mannanase Man5A increases the mannan-hydrolysis of complex substrates.J Biotechnol. 2003 Feb 27;101(1):37-48. doi: 10.1016/s0168-1656(02)00290-0. J Biotechnol. 2003. PMID: 12523968
-
A review of the enzymatic hydrolysis of mannans and synergistic interactions between β-mannanase, β-mannosidase and α-galactosidase.World J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2015 Aug;31(8):1167-75. doi: 10.1007/s11274-015-1878-2. Epub 2015 May 31. World J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2015. PMID: 26026279 Review.
-
Microbial mannanases: an overview of production and applications.Crit Rev Biotechnol. 2007 Oct-Dec;27(4):197-216. doi: 10.1080/07388550701775919. Crit Rev Biotechnol. 2007. PMID: 18085462 Review.
Cited by
-
Gene-Phenotype Associations Involving Human-Residential Bifidobacteria (HRB) Reveal Significant Species- and Strain-Specificity in Carbohydrate Catabolism.Microorganisms. 2021 Apr 21;9(5):883. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms9050883. Microorganisms. 2021. PMID: 33919102 Free PMC article.
-
Origin, evolution, and divergence of plant class C GH9 endoglucanases.BMC Evol Biol. 2018 May 30;18(1):79. doi: 10.1186/s12862-018-1185-2. BMC Evol Biol. 2018. PMID: 29848310 Free PMC article.
-
Structure and evolution of the bifidobacterial carbohydrate metabolism proteins and enzymes.Biochem Soc Trans. 2021 Apr 30;49(2):563-578. doi: 10.1042/BST20200163. Biochem Soc Trans. 2021. PMID: 33666221 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Functional diversity of three tandem C-terminal carbohydrate-binding modules of a β-mannanase.J Biol Chem. 2021 Jan-Jun;296:100638. doi: 10.1016/j.jbc.2021.100638. Epub 2021 Apr 7. J Biol Chem. 2021. PMID: 33838183 Free PMC article.
-
Proteinaceous Molecules Mediating Bifidobacterium-Host Interactions.Front Microbiol. 2016 Aug 3;7:1193. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2016.01193. eCollection 2016. Front Microbiol. 2016. PMID: 27536282 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Lundqvist J, Teleman A, Junel L, Zacchi G, Dahlman O, Tjerneld F, et al. Isolation and characterization of galactoglucomannan from spruce (Picea abies) Carbohydr Polym. 2002;48:29–39. doi: 10.1016/S0144-8617(01)00210-7. - DOI
-
- Cherubini F. The biorefinery concept: Using biomass instead of oil for producing energy and chemicals. Energy Conv Manage. 2010;51(7):1412–21. doi: 10.1016/j.enconman.2010.01.015. - DOI
-
- Yamabhai M, S S-U, W S, Haltrich D. Mannan biotechnology: from biofuels to health. Crit Rev Biotechnol. 2014:1-11 [Epub ahead of print]. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

